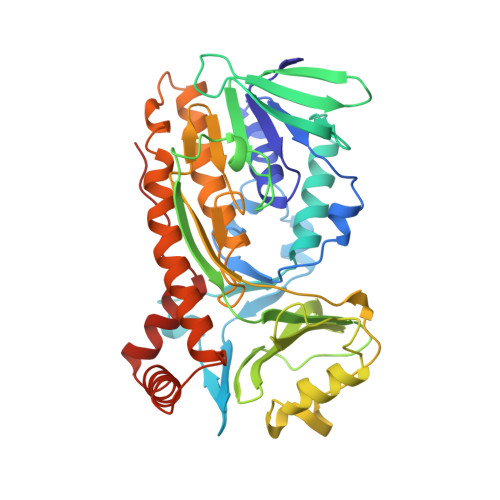
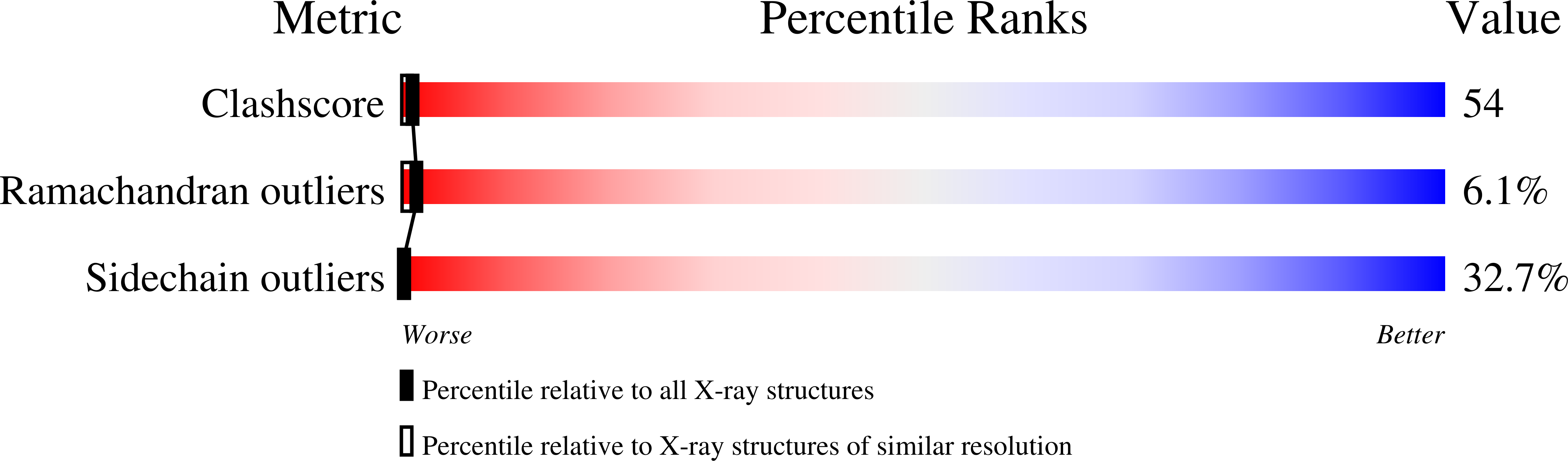Crystal structure of p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase complexed with its reaction product 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate.
Schreuder, H.A., van der Laan, J.M., Hol, W.G., Drenth, J.(1988) J Mol Biol 199: 637-648
- PubMed: 3351945
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(88)90307-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PHH - PubMed Abstract:
Crystals of the flavin-containing enzyme p-hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase (PHBHase) complexed with its reaction product were investigated in order to obtain insight into the catalytic cycle of this enzyme involving two substrates and two cofactors. PHBHase was crystallized initially with its substrate, p-hydroxybenzoate and the substrate was then converted into the product 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate by allowing the catalytic reaction to proceed in the crystals. In addition, crystals were soaked in mother liquor containing a high concentration of this product. Data up to 2.3 A (1 A = 0.1 nm) were collected by the oscillation method and the structure of the enzyme product complex was refined by alternate restrained least-squares procedures and model building by computer graphics techniques. A total of 273 solvent molecules could be located, four of them being presumably sulfate ions. The R-factor for 14,339 reflections between 6.0 A and 2.3 A is 19.3%. The 3-hydroxyl group of the product introduced by the enzyme is clearly visible in the electron density, showing unambiguously which carbon atom of the substrate is hydroxylated. A clear picture of the hydroxylation site is obtained. The plane of the product is rotated 21 degrees with respect to the plane of the substrate in the current model of enzyme-substrate complex. The 4-hydroxyl group of the product is hydrogen bonded to the hydroxyl group of Tyr201, its carboxyl group is interacting with the side-chains of Tyr222, Arg214 and Ser212, while the newly introduced 3-hydroxyl group makes a hydrogen bond with the backbone carbonyl oxygen of Pro293.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Chemical Physics, University of Groningen, The Netherlands.