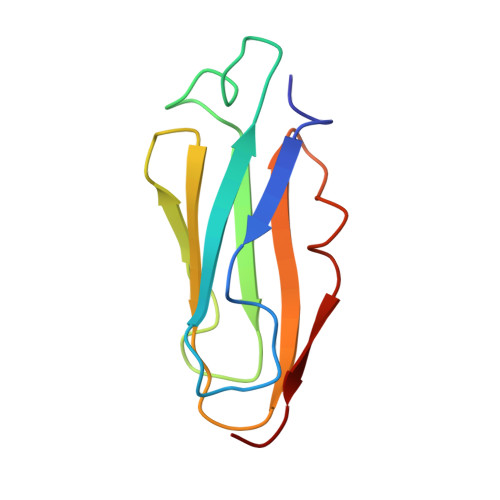
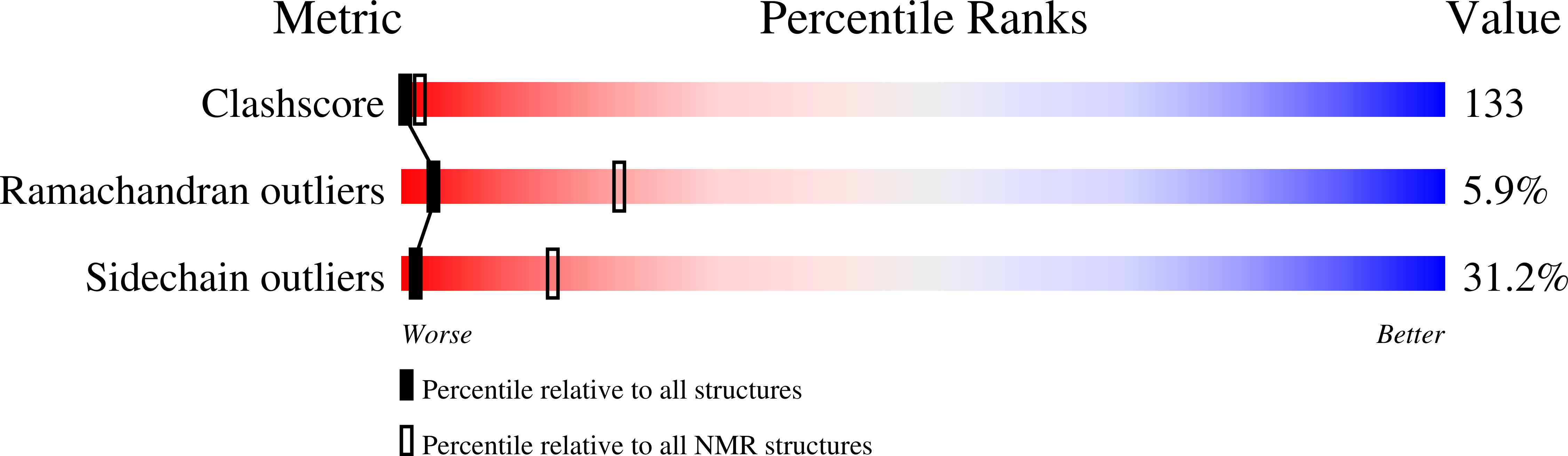The repeating segments of the F-actin cross-linking gelation factor (ABP-120) have an immunoglobulin-like fold.
Fucini, P., Renner, C., Herberhold, C., Noegel, A.A., Holak, T.A.(1997) Nat Struct Biol 4: 223-230
- PubMed: 9164464
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0397-223
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KSR - PubMed Abstract:
The 120,000 M(r) gelation factor and alpha-actinin are among the most abundant F-actin cross-linking proteins in Dictyostelium discoideum. Both molecules are rod-shaped homodimers. Each monomer chain is comprised of an actin-binding domain and a rod domain. The rod domain of the gelation factor consists of six 100-residue repetitive segments with high internal homology. We have now determined the three-dimensional structure of segment 4 of the rod domain of the gelation factor from D. discoideum using NMR spectroscopy. The segment consists of seven beta-sheets arranged in an immunoglobulin-like (Ig) fold. This is completely different from the alpha-actinin rod domain which consists of four spectrin-like alpha-helical segments. The gelation factor is the first example of an Ig-fold found in an actin-binding protein. Two highly homologous actin-binding proteins from human with similar sequences to the gelation factor, filamin and a 280,000 M(r) actin-binding protein (ABP-280), share conserved residues that form the core of the gelation factor repetitive segment structure. Thus, the segment 4 structure should be common to this subfamily of the spectrin superfamily. The structure of segment 4 together with previously published electron microscopy data, provide an explanation for the dimerization of the whole gelation factor molecule.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max Planck Institute for Biochemistry, Martinsried, F.R.G.