On the effect of covalently appended quinolones on termini of DNA duplexes.
Tuma, J., Connors, W.H., Stitelman, D.H., Richert, C.(2002) J Am Chem Soc 124: 4236-4246
- PubMed: 11960452
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0125117
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KSE - PubMed Abstract:
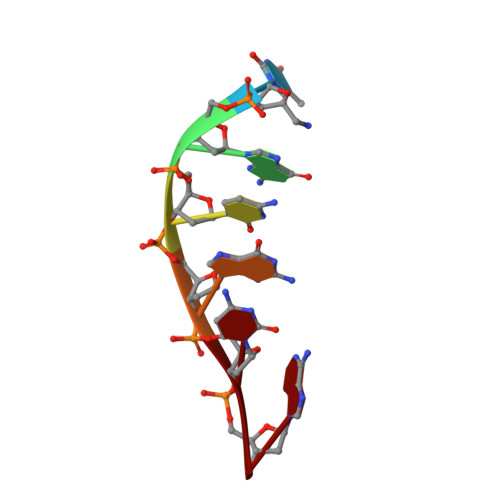
Quinolones are gyrase inhibitors that are widely used as antibiotics in the clinic. When covalently attached to oligonucleotides as 5'-acylamido substituents, quinolones were found to stabilize duplexes of oligonucleotides against thermal denaturation. For short duplexes, such as qu-T*GCGCA, where qu is a quinolone residue and T is a 5'-amino-5'-deoxythymidine residue, an increase in the UV melting point of up to 27.8 degrees C was measured. The stabilizing effect was demonstrated for all quinolones tested, namely nalidixic acid, oxolinic acid, pipemidic acid, cinoxacin, norfloxacin, and ofloxacin. The three-dimensional structure of (oa-T*GCGCA)2, where oa is an oxolinic acid residue, was solved by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy and restrained molecular dynamics. In this complex, the oxolinic acid residues disrupt the terminal T1:A6 base pairs and stack on the G2:C5 base pairs. The displaced adenosine residues bind in the minor groove of the core duplex, while the thymidine residues pack against the oxolinic acid residues. The "molecular cap" thus formed fits tightly on the G:C base pairs, resulting in increased base-pairing fidelity, as demonstrated in UV melting experiments with the sequence oa-T*GGTTGAC and target strands containing a mismatched nucleobase. The structure of the "molecular cap" with its disrupted terminal base pair may also be helpful for modeling how quinolones block re-ligation of DNA strands in the active site of gyrases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Constance, Fach M 709, D-78457 Konstanz, Germany.