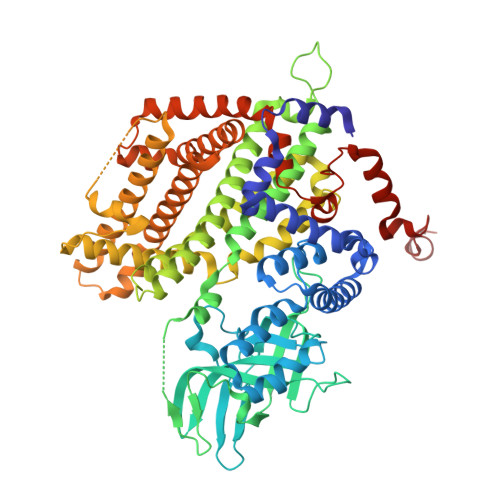
Three-dimensional structure of the flavoenzyme acyl-CoA oxidase-II from rat liver, the peroxisomal counterpart of mitochondrial acyl-CoA dehydrogenase.
Nakajima, Y., Miyahara, I., Hirotsu, K., Nishina, Y., Shiga, K., Setoyama, C., Tamaoki, H., Miura, R.(2002) J Biochem 131: 365-374
- PubMed: 11872165
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a003111
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IS2 - PubMed Abstract:
Acyl-CoA oxidase (ACO) catalyzes the first and rate-determining step of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation of fatty acids. The crystal structure of ACO-II, which is one of two forms of rat liver ACO (ACO-I and ACO-II), has been solved and refined to an R-factor of 20.6% at 2.2-A resolution. The enzyme is a homodimer, and the polypeptide chain of the subunit is folded into the N-terminal alpha-domain, beta-domain, and C-terminal alpha-domain. The X-ray analysis showed that the overall folding of ACO-II less C-terminal 221 residues is similar to that of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD). However, the N-terminal alpha- and beta-domains rotate by 13 with respect to the C-terminal alpha-domain compared with those in MCAD to give a long and large crevice that accommodates the cofactor FAD and the substrate acyl-CoA. FAD is bound to the crevice between the beta- and C-terminal domains with its adenosine diphosphate portion interacting extensively with the other subunit of the molecule. The flavin ring of FAD resides at the active site with its si-face attached to the beta-domain, and is surrounded by active-site residues in a mode similar to that found in MCAD. However, the residues have weak interactions with the flavin ring due to the loss of some of the important hydrogen bonds with the flavin ring found in MCAD. The catalytic residue Glu421 in the C-terminal alpha-domain seems to be too far away from the flavin ring to abstract the alpha-proton of the substrate acyl-CoA, suggesting that the C-terminal domain moves to close the active site upon substrate binding. The pyrimidine moiety of flavin is exposed to the solvent and can readily be attacked by molecular oxygen, while that in MCAD is protected from the solvent. The crevice for binding the fatty acyl chain is 28 A long and 6 A wide, large enough to accommodate the C23 acyl chain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Osaka City University, Sugimoto, Sumiyoshi-ku, Osaka 558-8585, Japan.