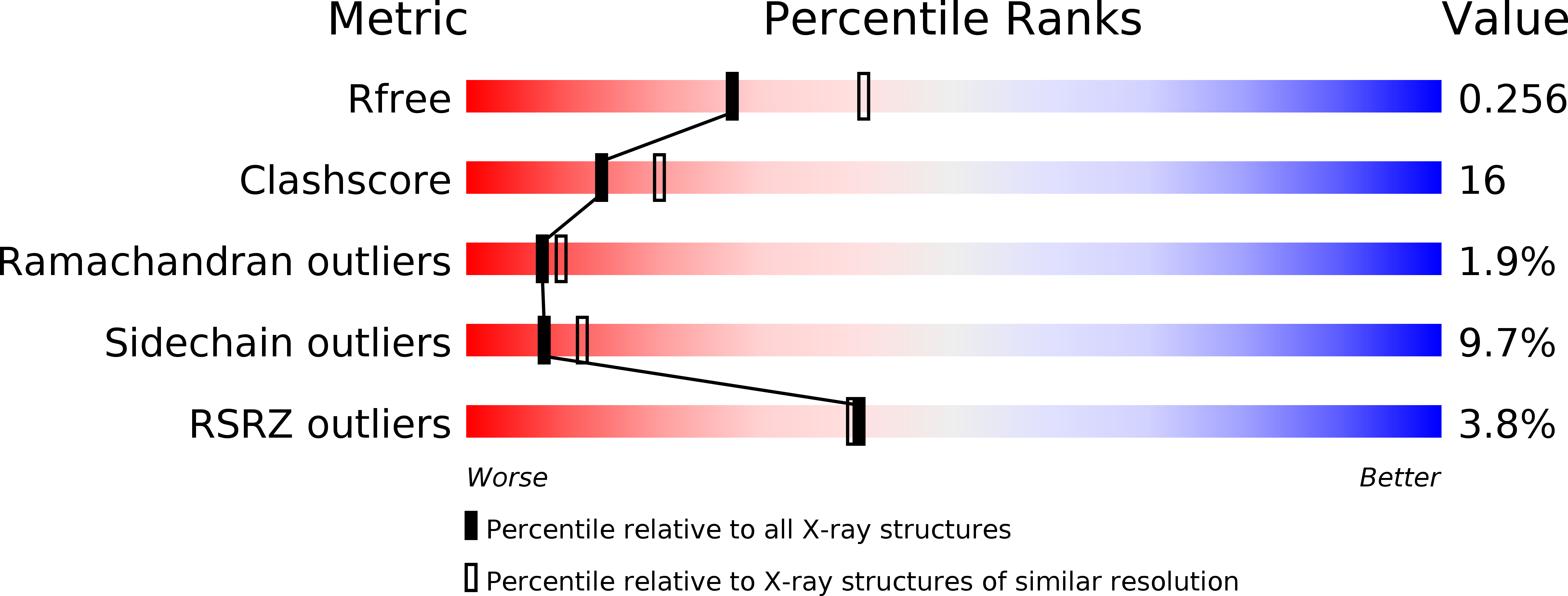
A novel pH-dependent dimerization motif in beta-lactoglobulin from pig (Sus scrofa).
Hoedemaeker, F.J., Visschers, R.W., Alting, A.C., de Kruif, K.G., Kuil, M.E., Abrahams, J.P.(2002) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58: 480-486
- PubMed: 11856834
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444902000616
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1EXS - PubMed Abstract:
beta-Lactoglobulin (BLG) is a lipocalin and is the major protein in the whey of the milk of cows and other ruminants, but not in all mammalian species. The biological function of BLG is not clear, but a potential role in carrying fatty acids through the digestive tract has been proposed. The capability of BLG to aggregate and form gels is often used to thicken foodstuffs. The structure of the porcine form is sufficiently different from other known BLG structures that SIRAS phases had to be measured in order to solve the crystal structure to 2.4 A resolution. The r.m.s. deviation of C(alpha) atoms is 2.8 A between porcine and bovine BLG. Nevertheless, the typical lipocalin fold is conserved. Compared with bovine BLG, the tilted alpha-helix alters the arrangement of surface residues of the porcine form, completely changing the dimerization behaviour. Through a unique pH-dependent domain-swapping mechanism involving the first ten residues, a novel dimer interface is formed at the N-terminus of porcine BLG. The existence of this novel dimer at low pH is supported by gel-filtration experiments. These results provide a rationale for the difference in physicochemical behaviour between bovine and porcine BLG and point the way towards engineering such dimerization motifs into other members of the lipocalin family.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysical and Structural Chemistry, Leiden Institute for Chemistry, Leiden University, Einsteinweg 55, PO Box 9502, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands. hoedemae@chem.leidenuniv.nl