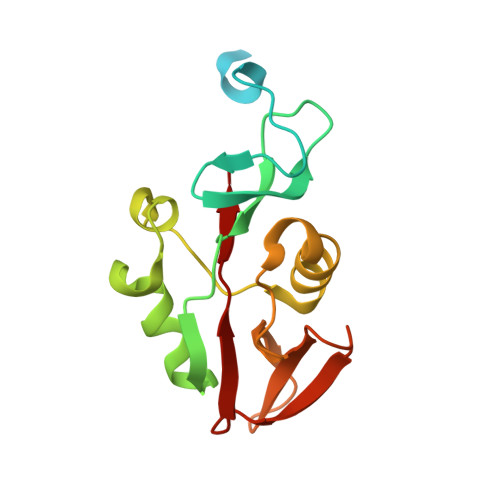
The Legionella collagen-like protein employs a unique binding mechanism for the recognition of host glycosaminoglycans.
Rehman, S., Antonovic, A.K., McIntire, I.E., Zheng, H., Cleaver, L., Adams, C.O., Portlock, T., Richardson, K., Shaw, R., Oregioni, A., Mastroianni, G., Whittaker, S.B., Kelly, G., Fornili, A., Cianciotto, N.P., Garnett, J.A.(2023) Biorxiv
- PubMed: 38106198
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.12.10.570962
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
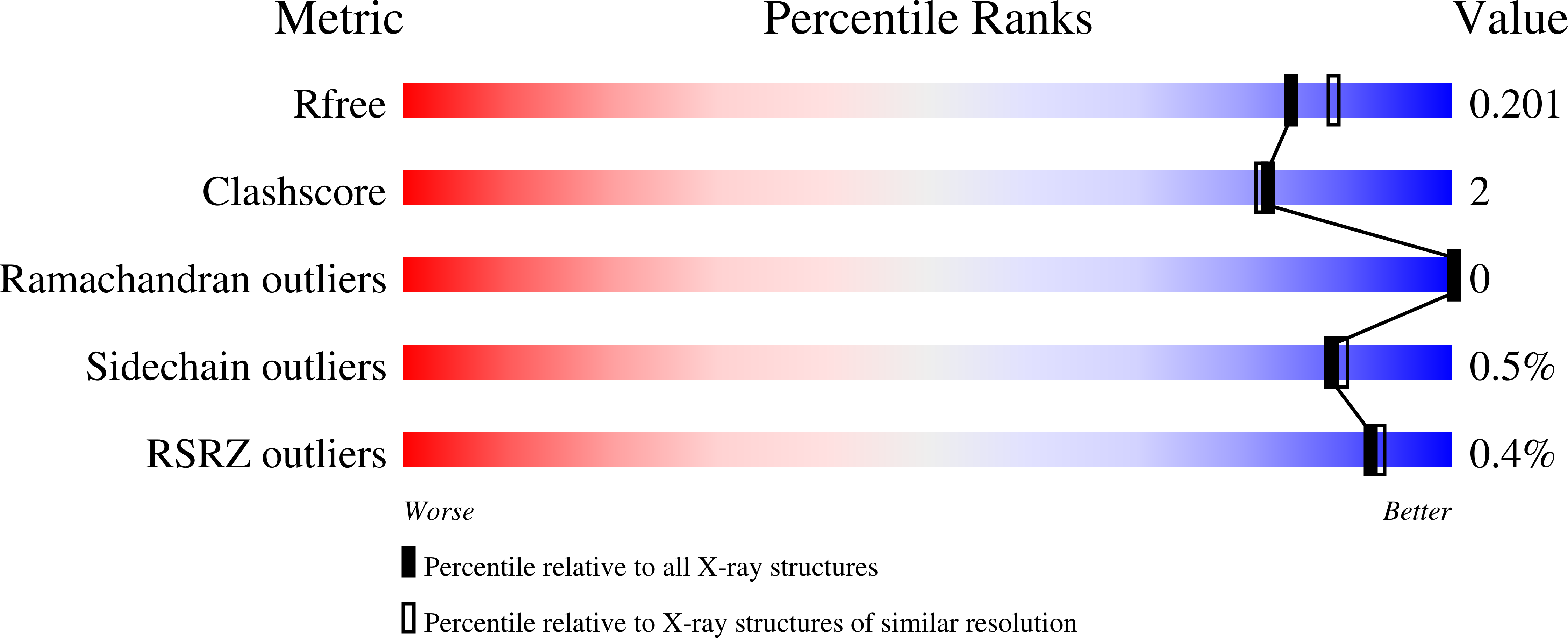
8Q4E, 8QK8 - PubMed Abstract:
Bacterial adhesion is a fundamental process which enables colonisation of niche environments and is key for infection. However, in Legionella pneumophila , the causative agent of Legionnaires' disease, these processes are not well understood. The Legionella collagen-like protein (Lcl) is an extracellular peripheral membrane protein that recognises sulphated glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) on the surface of eukaryotic cells, but also stimulates bacterial aggregation in response to divalent cations. Here we report the crystal structure of the Lcl C-terminal domain (Lcl-CTD) and present a model for intact Lcl. Our data reveal that Lcl-CTD forms an unusual dynamic trimer arrangement with a positively charged external surface and a negatively charged solvent exposed internal cavity. Through Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations, we show how the GAG chondroitin-4-sulphate associates with the Lcl-CTD surface via unique binding modes. Our findings show that Lcl homologs are present across both the Pseudomonadota and Fibrobacterota-Chlorobiota-Bacteroidota phyla and suggest that Lcl may represent a versatile carbohydrate binding mechanism.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre for Host-Microbiome Interactions, Faculty of Dental, Oral & Craniofacial Sciences, King's College London, London, UK.