BTB domain mutations perturbing KCTD15 oligomerisation cause a distinctive frontonasal dysplasia syndrome.
Miller, K.A., Cruz Walma, D.A., Pinkas, D.M., Tooze, R.S., Bufton, J.C., Richardson, W., Manning, C.E., Hunt, A.E., Cros, J., Hartill, V., Parker, M.J., McGowan, S.J., Twigg, S.R.F., Chalk, R., Staunton, D., Johnson, D., Wilkie, A.O.M., Bullock, A.N.(2024) J Med Genet 61: 490-501
- PubMed: 38296633
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg-2023-109531
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
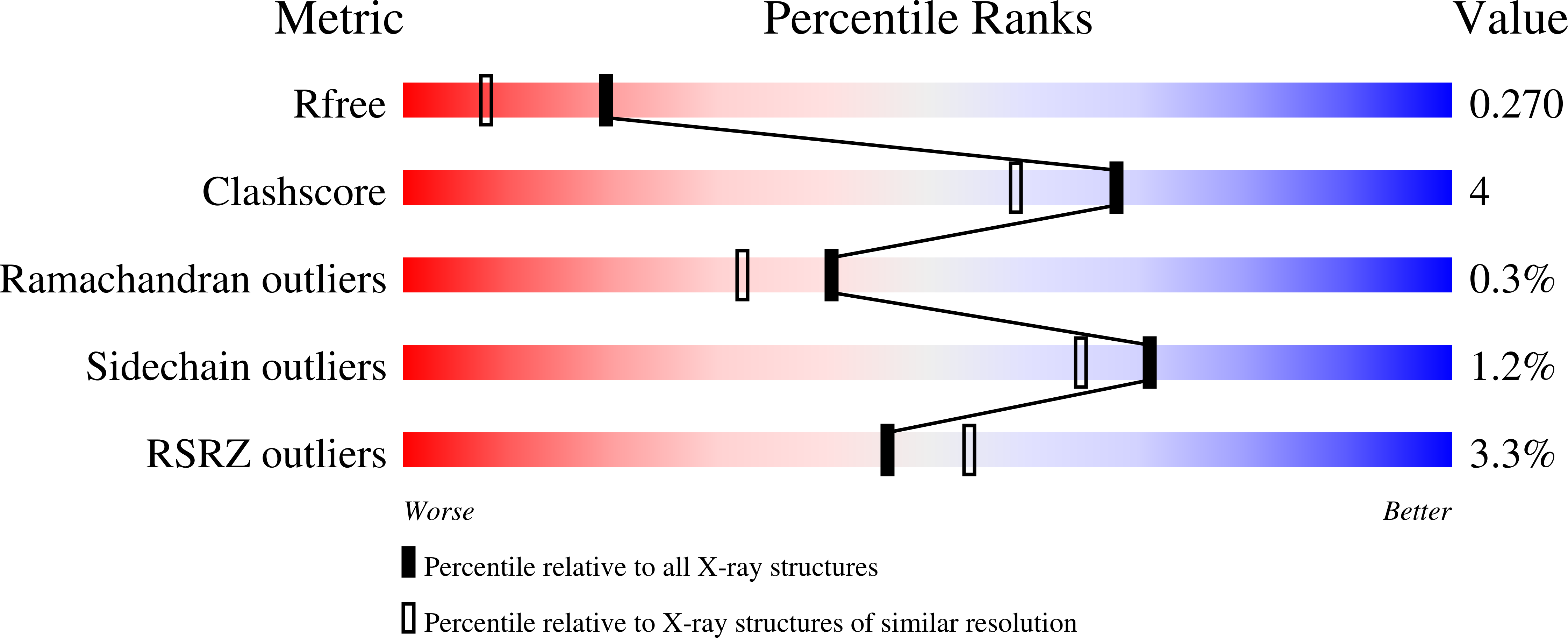
8PNM, 8PNR - PubMed Abstract:
KCTD15 encodes an oligomeric BTB domain protein reported to inhibit neural crest formation through repression of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling, as well as transactivation by TFAP2. Heterozygous missense variants in the closely related paralogue KCTD1 cause scalp-ear-nipple syndrome. Exome sequencing was performed on a two-generation family affected by a distinctive phenotype comprising a lipomatous frontonasal malformation, anosmia, cutis aplasia of the scalp and/or sparse hair, and congenital heart disease. Identification of a de novo missense substitution within KCTD15 led to targeted sequencing of DNA from a similarly affected sporadic patient, revealing a different missense mutation. Structural and biophysical analyses were performed to assess the effects of both amino acid substitutions on the KCTD15 protein. A heterozygous c.310G>C variant encoding p.(Asp104His) within the BTB domain of KCTD15 was identified in an affected father and daughter and segregated with the phenotype. In the sporadically affected patient, a de novo heterozygous c.263G>A variant encoding p.(Gly88Asp) was present in KCTD15. Both substitutions were found to perturb the pentameric assembly of the BTB domain. A crystal structure of the BTB domain variant p.(Gly88Asp) revealed a closed hexameric assembly, whereas biophysical analyses showed that the p.(Asp104His) substitution resulted in a monomeric BTB domain likely to be partially unfolded at physiological temperatures. BTB domain substitutions in KCTD1 and KCTD15 cause clinically overlapping phenotypes involving craniofacial abnormalities and cutis aplasia. The structural analyses demonstrate that missense substitutions act through a dominant negative mechanism by disrupting the higher order structure of the KCTD15 protein complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK.