Sialidases and fucosidases of Akkermansia muciniphila are crucial for growth on mucin and nutrient sharing with mucus-associated gut bacteria.
Shuoker, B., Pichler, M.J., Jin, C., Sakanaka, H., Wu, H., Gascuena, A.M., Liu, J., Nielsen, T.S., Holgersson, J., Nordberg Karlsson, E., Juge, N., Meier, S., Morth, J.P., Karlsson, N.G., Abou Hachem, M.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 1833-1833
- PubMed: 37005422
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37533-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
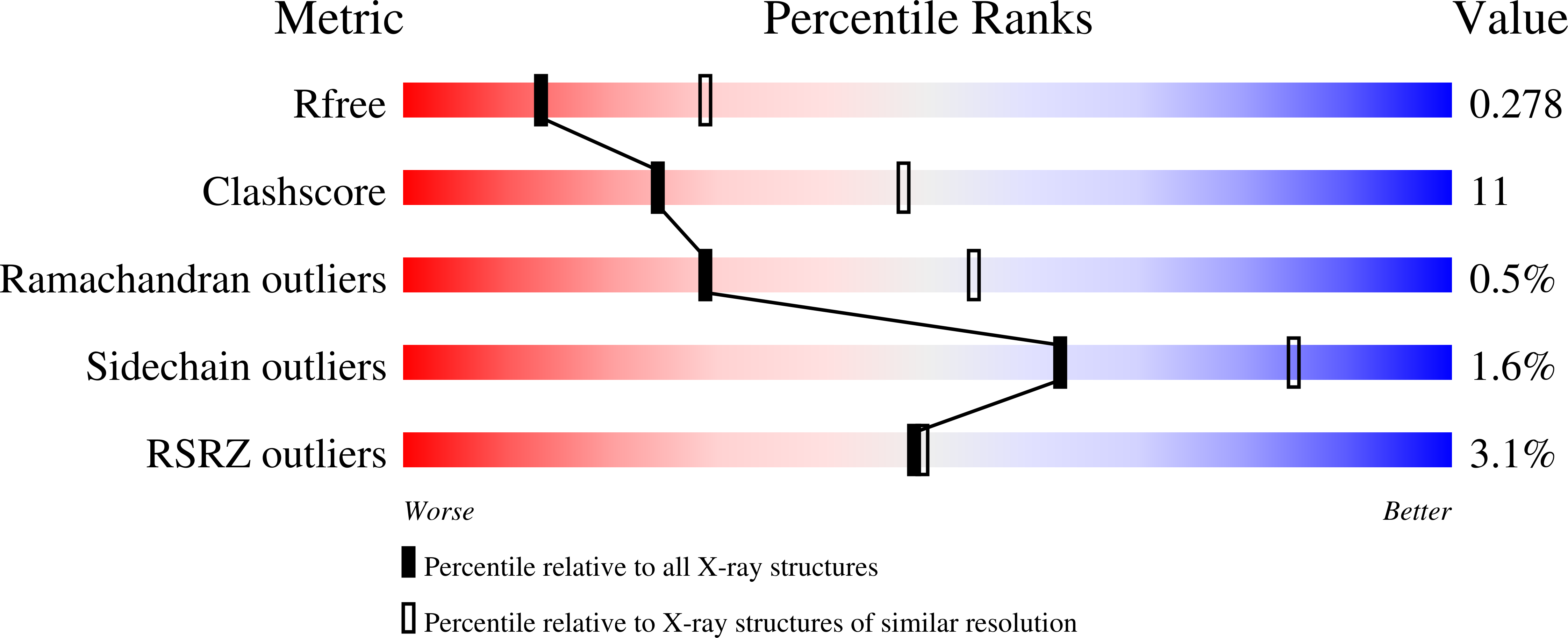
8AXI, 8AXS, 8AXT, 8AYR - PubMed Abstract:
The mucolytic human gut microbiota specialist Akkermansia muciniphila is proposed to boost mucin-secretion by the host, thereby being a key player in mucus turnover. Mucin glycan utilization requires the removal of protective caps, notably fucose and sialic acid, but the enzymatic details of this process remain largely unknown. Here, we describe the specificities of ten A. muciniphila glycoside hydrolases, which collectively remove all known sialyl and fucosyl mucin caps including those on double-sulfated epitopes. Structural analyses revealed an unprecedented fucosidase modular arrangement and explained the sialyl T-antigen specificity of a sialidase of a previously unknown family. Cell-attached sialidases and fucosidases displayed mucin-binding and their inhibition abolished growth of A. muciniphila on mucin. Remarkably, neither the sialic acid nor fucose contributed to A. muciniphila growth, but instead promoted butyrate production by co-cultured Clostridia. This study brings unprecedented mechanistic insight into the initiation of mucin O-glycan degradation by A. muciniphila and nutrient sharing between mucus-associated bacteria.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biotechnology and Biomedicine, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, 2800, Denmark.