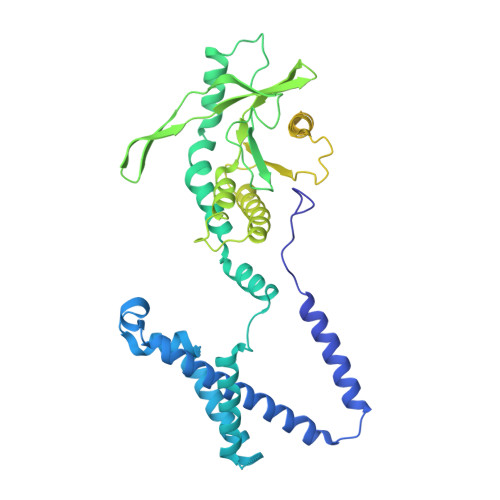
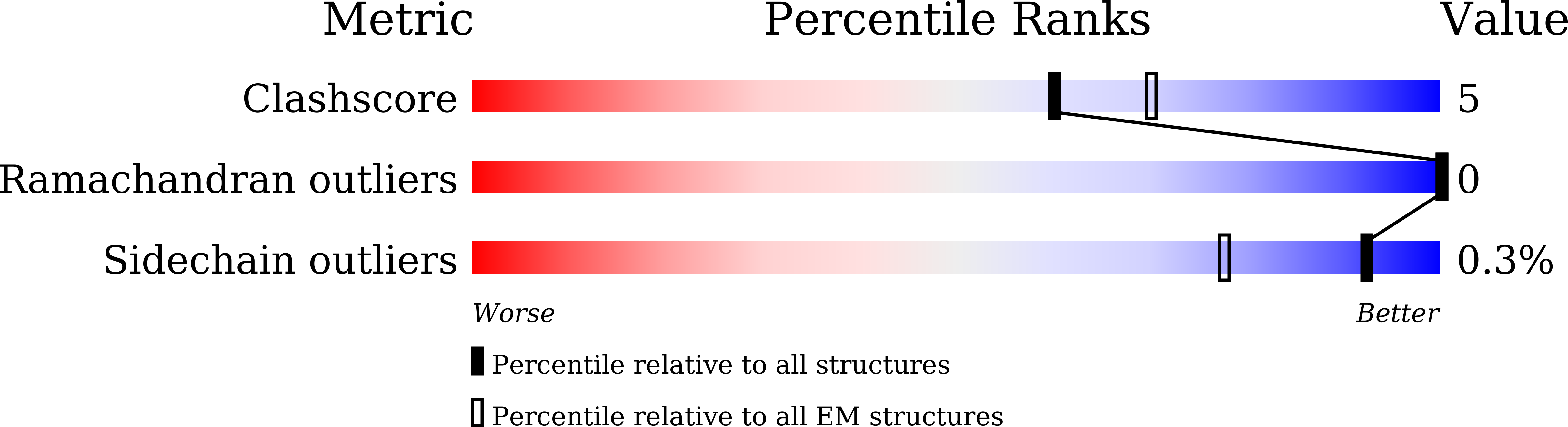The mechanism of STING autoinhibition and activation.
Liu, S., Yang, B., Hou, Y., Cui, K., Yang, X., Li, X., Chen, L., Liu, S., Zhang, Z., Jia, Y., Xie, Y., Xue, Y., Li, X., Yan, B., Wu, C., Deng, W., Qi, J., Lu, D., Gao, G.F., Wang, P., Shang, G.(2023) Mol Cell 83: 1502-1518.e10
- PubMed: 37086726
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2023.03.029
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8IK0, 8IK3 - PubMed Abstract:
2',3'-cGAMP, produced by the DNA sensor cGAS, activates stimulator of interferon genes (STING) and triggers immune response during infection. Tremendous effort has been placed on unraveling the mechanism of STING activation. However, little is known about STING inhibition. Here, we found that apo-STING exhibits a bilayer with head-to-head as well as side-by-side packing, mediated by its ligand-binding domain (LBD). This type of assembly holds two endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membranes together not only to prevent STING ER exit but also to eliminate the recruitment of TBK1, representing the autoinhibited state of STING. Additionally, we obtained the filament structure of the STING/2',3'-cGAMP complex, which adopts a bent monolayer assembly mediated by LBD and transmembrane domain (TMD). The active, curved STING polymer could deform ER membrane to support its ER exit and anterograde transportation. Our data together provide a panoramic vision regarding STING autoinhibition and activation, which adds substantially to current understanding of the cGAS-STING pathway.
Organizational Affiliation:
Shanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Protein Structure Determination, Shanxi Academy of Advanced Research and Innovation, Taiyuan 030012, China; CAS Key Laboratory of Pathogen Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China; Cryo-EM Center, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China.