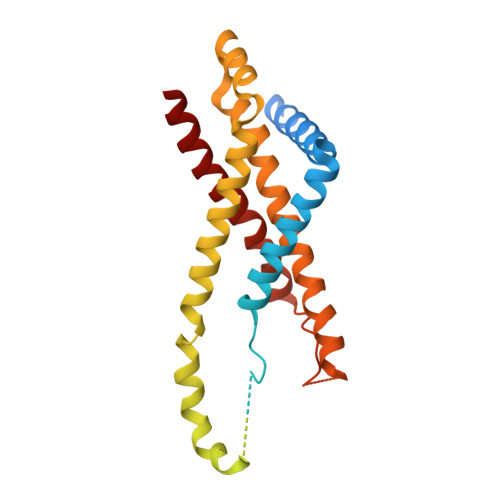
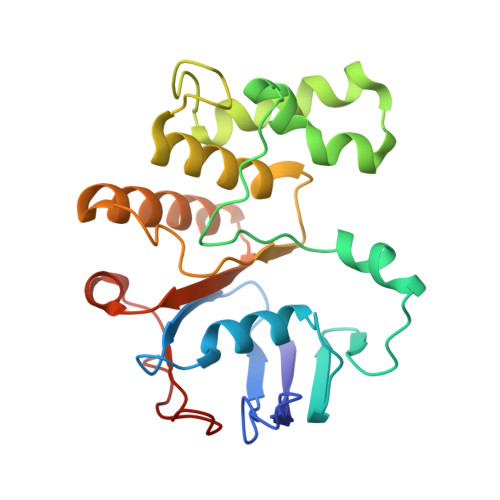
Mechanistic insights into the regulation of cell wall hydrolysis by FtsEX and EnvC at the bacterial division site.
Xu, X., Li, J., Chua, W.Z., Pages, M.A., Shi, J., Hermoso, J.A., Bernhardt, T., Sham, L.T., Luo, M.(2023) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 120: e2301897120-e2301897120
- PubMed: 37186861
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2301897120
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8I6O, 8I6Q, 8I6R, 8I6S - PubMed Abstract:
The peptidoglycan (PG) cell wall produced by the bacterial division machinery is initially shared between the daughters and must be split to promote cell separation and complete division. In gram-negative bacteria, enzymes that cleave PG called amidases play major roles in the separation process. To prevent spurious cell wall cleavage that can lead to cell lysis, amidases like AmiB are autoinhibited by a regulatory helix. Autoinhibition is relieved at the division site by the activator EnvC, which is in turn regulated by the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter-like complex called FtsEX. EnvC is also known to be autoinhibited by a regulatory helix (RH), but how its activity is modulated by FtsEX and the mechanism by which it activates the amidases have remained unclear. Here, we investigated this regulation by determining the structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa FtsEX alone with or without bound ATP, in complex with EnvC, and in a FtsEX-EnvC-AmiB supercomplex. In combination with biochemical studies, the structures reveal that ATP binding is likely to activate FtsEX-EnvC and promote its association with AmiB. Furthermore, the AmiB activation mechanism is shown to involve a RH rearrangement. In the activated state of the complex, the inhibitory helix of EnvC is released, freeing it to associate with the RH of AmiB, which liberates its active site for PG cleavage. These regulatory helices are found in many EnvC proteins and amidases throughout gram-negative bacteria, suggesting that the activation mechanism is broadly conserved and a potential target for lysis-inducing antibiotics that misregulate the complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117543.