Structural and binding studies of a new chitin-active AA10 lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase from the marine bacterium Vibrio campbellii.
Zhou, Y., Wannapaiboon, S., Prongjit, M., Pornsuwan, S., Sucharitakul, J., Kamonsutthipaijit, N., Robinson, R.C., Suginta, W.(2023) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 79: 479-497
- PubMed: 37259836
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798323003261
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8GUL, 8GUM - PubMed Abstract:
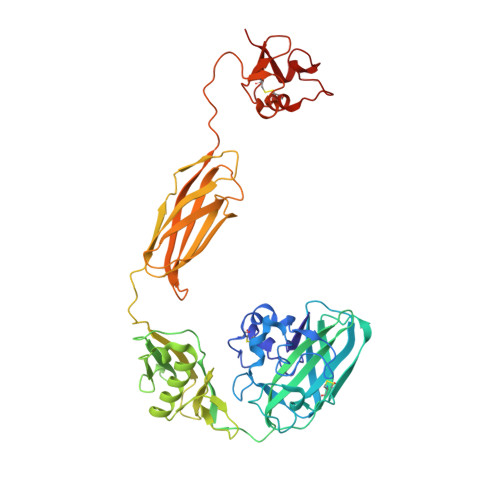
Vibrio spp. play a crucial role in the global recycling of the highly abundant recalcitrant biopolymer chitin in marine ecosystems through their ability to secrete chitin-degrading enzymes to efficiently hydrolyse chitinous materials and use them as their major carbon source. In this study, the first crystal structures of a complete four-domain chitin-active AA10 lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase from the chitinolytic bacterium Vibrio campbellii type strain ATCC BAA-1116 are reported. The crystal structures of apo and copper-bound VhLPMO10A were resolved as homodimers with four distinct domains: an N-terminal AA10 catalytic (CatD) domain connected to a GlcNAc-binding (GbpA_2) domain, followed by a module X domain and a C-terminal carbohydrate-binding module (CBM73). Size-exclusion chromatography and small-angle X-ray scattering analysis confirmed that VhLPMO10A exists as a monomer in solution. The active site of VhLPMO10A is located on the surface of the CatD domain, with three conserved residues (His1, His98 and Phe170) forming the copper(II)-binding site. Metal-binding studies using synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray fluorescence, together with electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, gave consistently strong copper(II) signals in the protein samples, confirming that VhLPMO10A is a copper-dependent enzyme. ITC binding data showed that VhLPMO10A could bind various divalent cations but bound most strongly to copper(II) ions, with a K d of 0.1 ± 0.01 µM. In contrast, a K d of 1.9 nM was estimated for copper(I) ions from redox-potential measurements. The presence of ascorbic acid is essential for H 2 O 2 production in the reaction catalysed by VhLPMO10A. MALDI-TOF MS identified VhLPMO10A as a C1-specific LPMO, generating oxidized chitooligosaccharide products with different degrees of polymerization (DP2 ox -DP8 ox ). This new member of the chitin-active AA10 LPMOs could serve as a powerful biocatalyst in biofuel production from chitin biomass.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biomolecular Science and Engineering (BSE), Vidyasirimedhi Institute of Science and Technology, Rayong 21210, Thailand.