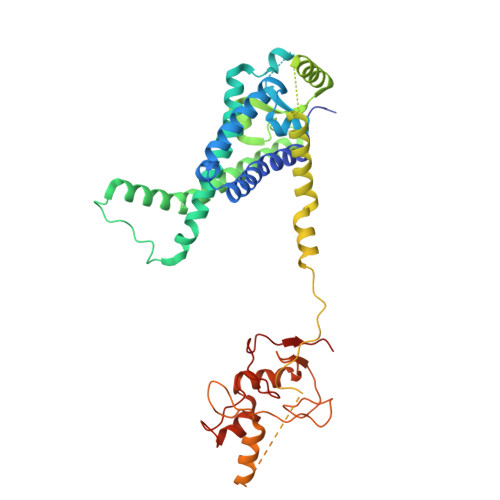
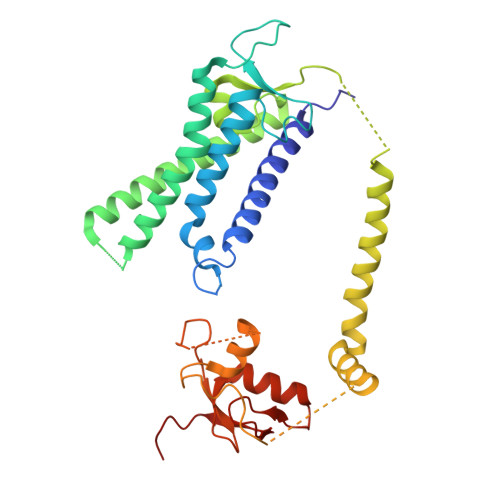
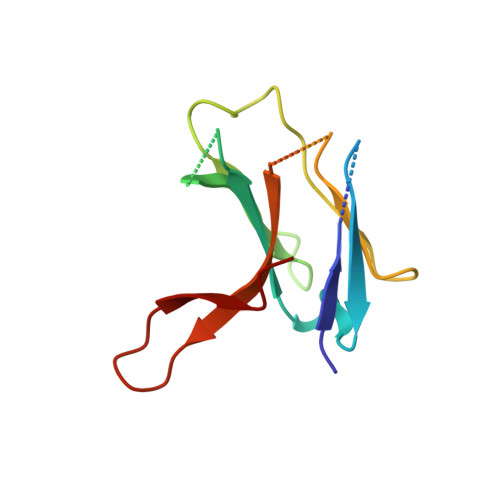
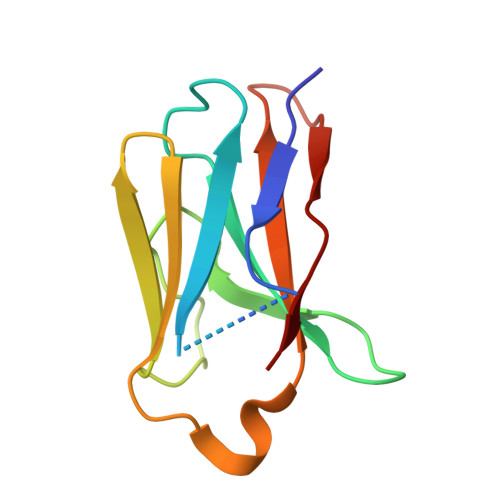
A peroxisomal ubiquitin ligase complex forms a retrotranslocation channel.
Feng, P., Wu, X., Erramilli, S.K., Paulo, J.A., Knejski, P., Gygi, S.P., Kossiakoff, A.A., Rapoport, T.A.(2022) Nature 607: 374-380
- PubMed: 35768507
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04903-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7T92, 7T9X - PubMed Abstract:
Peroxisomes are ubiquitous organelles that house various metabolic reactions and are essential for human health 1-4 . Luminal peroxisomal proteins are imported from the cytosol by mobile receptors, which then recycle back to the cytosol by a poorly understood process 1-4 . Recycling requires receptor modification by a membrane-embedded ubiquitin ligase complex comprising three RING finger domain-containing proteins (Pex2, Pex10 and Pex12) 5,6 . Here we report a cryo-electron microscopy structure of the ligase complex, which together with biochemical and in vivo experiments reveals its function as a retrotranslocation channel for peroxisomal import receptors. Each subunit of the complex contributes five transmembrane segments that co-assemble into an open channel. The three ring finger domains form a cytosolic tower, with ring finger 2 (RF2) positioned above the channel pore. We propose that the N terminus of a recycling receptor is inserted from the peroxisomal lumen into the pore and monoubiquitylated by RF2 to enable extraction into the cytosol. If recycling is compromised, receptors are polyubiquitylated by the concerted action of RF10 and RF12 and degraded. This polyubiquitylation pathway also maintains the homeostasis of other peroxisomal import factors. Our results clarify a crucial step during peroxisomal protein import and reveal why mutations in the ligase complex cause human disease.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cell Biology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA. peiqiang_feng@hms.harvard.edu.