Specificity of Small c -Type Cytochromes in Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation.
Akram, M., Bock, J., Dietl, A., Barends, T.R.M.(2021) ACS Omega 6: 21457-21464
- PubMed: 34471748
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c02275
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
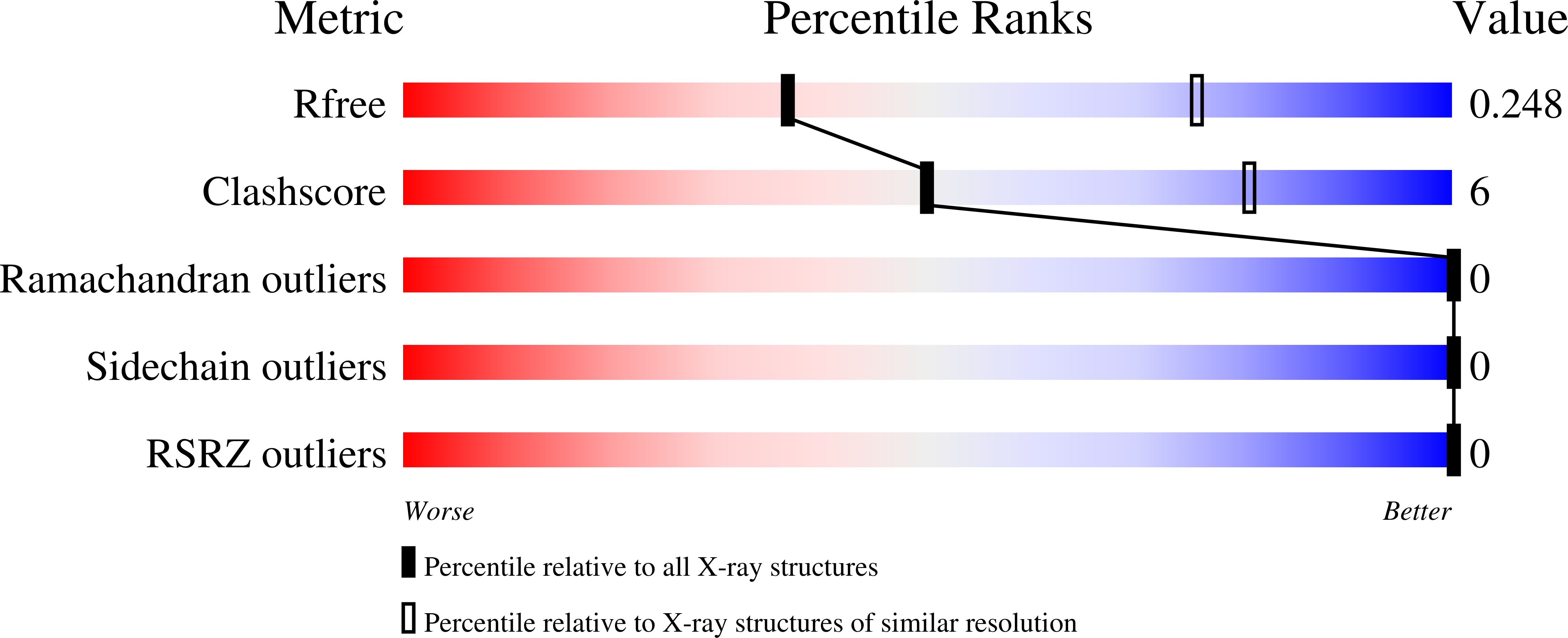
5MXY, 7O38 - PubMed Abstract:
Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) is a bacterial process in which ammonium and nitrite are combined into dinitrogen gas and water, yielding energy for the cell. This process relies on a series of redox reactions catalyzed by a set of enzymes, with electrons being shuttled to and from these enzymes, likely by small cytochrome c proteins. For this system to work productively, these electron carriers require a degree of specificity toward the various possible redox partners they encounter in the cell. Here, we compare two cytochrome c proteins from the anammox model organism Kuenenia stuttgartiensis . We show that they are highly homologous, are expressed at comparable levels, share the same fold, and display highly similar redox potentials, yet one of them accepts electrons from the metabolic enzyme hydroxylamine oxidase (HAO) efficiently, whereas the other does not. An analysis of the crystal structures supplemented by Monte Carlo simulations of the transient redox interactions suggests that this difference is at least partly due to the electrostatic field surrounding the proteins, illustrating one way in which the electron carriers in anammox could attain the required specificity. Moreover, the simulations suggest a different "outlet" for electrons on HAO than has traditionally been assumed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biomolecular Mechanisms, Max Planck Institute for Medical Research, Jahnstrasse 29, D-69120 Heidelberg, Germany.