Cell free protein synthesis versus yeast expression - A comparison using insulin as a model protein.
Jensen, A.B., Hubalek, F., Stidsen, C.E., Johansson, E., Oberg, F.K., Skjot, M., Kjeldsen, T.(2021) Protein Expr Purif 186: 105910-105910
- PubMed: 34089870
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2021.105910
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
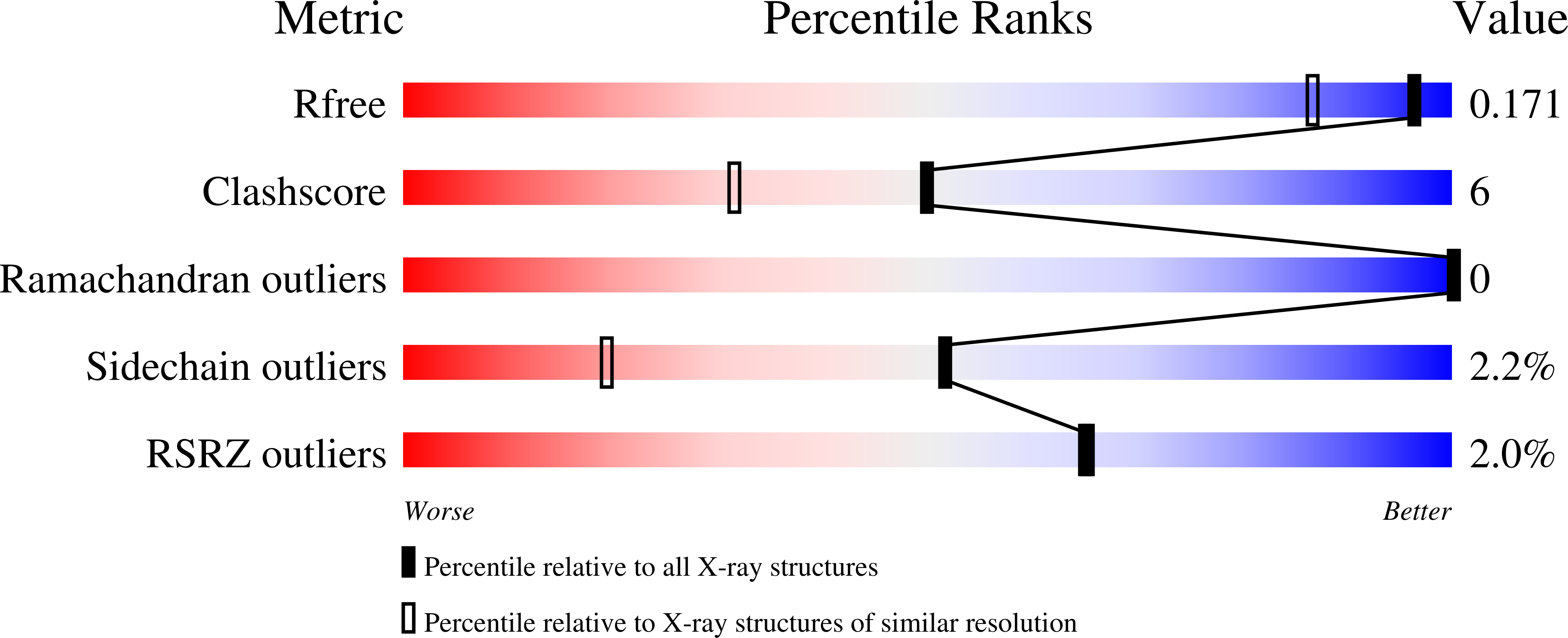
7NHU - PubMed Abstract:
Expression of recombinant proteins traditionally require a cellular system to transcribe and translate foreign DNA to a desired protein. The process requires special knowledge of the specific cellular metabolism in use and is often time consuming and labour intensive. A cell free expression system provides an opportunity to express recombinant proteins without consideration of the living cell. Instead, a cell free system relies on either a cellular lysate or recombinant proteins to carry out protein synthesis, increasing overall production speed and ease of handling. The one-pot cell free setup is commonly known as an in vitro transcription/translation reaction (IVTT). Here we focused on a PURE (Protein synthesis Using Recombinant Elements) IVTT system based on recombinant proteins from Escherichia coli. We evaluated the cell free system's ability to express functional insulin analogues compared to Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a well-established system for large scale production of recombinant human insulin and insulin analogues. Significantly, it was found that correct insulin expression and folding was governed by the inherent properties of the primary amino acids sequence of insulin, whereas the eukaryotic features of the expression system apparently play a minor role. The IVTT system successfully produced insulin analogues identical in structure and with similar insulin receptor affinity to those produced by yeast. In conclusion we demonstrate that the PURE IVTT system is highly suited for expressing soluble molecules with higher order features and multiple disulphide bridges.
Organizational Affiliation:
Novo Nordisk, A/S Novo Nordisk Park, DK-2760, Måløv, Denmark. Electronic address: asdj@novonordisk.com.