Comparative structural, biophysical, and receptor binding study of true type and wild type AAV2.
Bennett, A., Hull, J., Jolinon, N., Tordo, J., Moss, K., Binns, E., Mietzsch, M., Hagemann, C., Linden, R.M., Serio, A., Chipman, P., Sousa, D., Broecker, F., Seeberger, P., Henckaerts, E., McKenna, R., Agbandje-McKenna, M.(2021) J Struct Biol 213: 107795-107795
- PubMed: 34509611
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2021.107795
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7NA6 - PubMed Abstract:
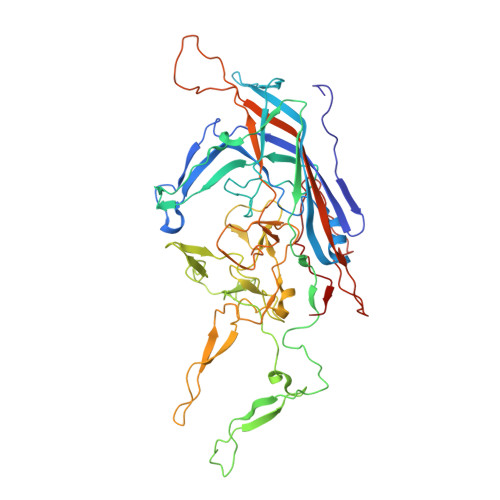
Adeno-associated viruses (AAV) are utilized as gene transfer vectors in the treatment of monogenic disorders. A variant, rationally engineered based on natural AAV2 isolates, designated AAV-True Type (AAV-TT), is highly neurotropic compared to wild type AAV2 in vivo, and vectors based on it, are currently being evaluated for central nervous system applications. AAV-TT differs from AAV2 by 14 amino acids, including R585S and R588T, two residues previously shown to be essential for heparan sulfate binding of AAV2. The capsid structures of AAV-TT and AAV2 visualized by cryo-electron microscopy at 3.4 and 3.0 Å resolution, respectively, highlighted structural perturbations at specific amino acid differences. Differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF) performed at different pH conditions demonstrated that the melting temperature (T m ) of AAV2 was consistently ∼5 °C lower than AAV-TT, but both showed maximal stability at pH 5.5, corresponding to the pH in the late endosome, proposed as required for VP1u externalization to facilitate endosomal escape. Reintroduction of arginines at positions 585 and 588 in AAV-TT caused a reduction in T m , demonstrating that the lack of basic amino acids at these positions are associated with capsid stability. These results provide structural and thermal annotation of AAV2/AAV-TT residue differences, that account for divergent cell binding, transduction, antigenic reactivity, and transduction of permissive tissues between the two viruses. Specifically, these data indicate that AAV-TT may not utilize a glycan receptor mediated pathway to enter cells and may have lower antigenic properties as compared to AAV2.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, Center for Structural Biology, The McKnight Brain Institute, College of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32610, USA.