Preferential CEBP binding to T:G mismatches and increased C-to-T human somatic mutations.
Yang, J., Horton, J.R., Akdemir, K.C., Li, J., Huang, Y., Kumar, J., Blumenthal, R.M., Zhang, X., Cheng, X.(2021) Nucleic Acids Res 49: 5084-5094
- PubMed: 33877329
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab276
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
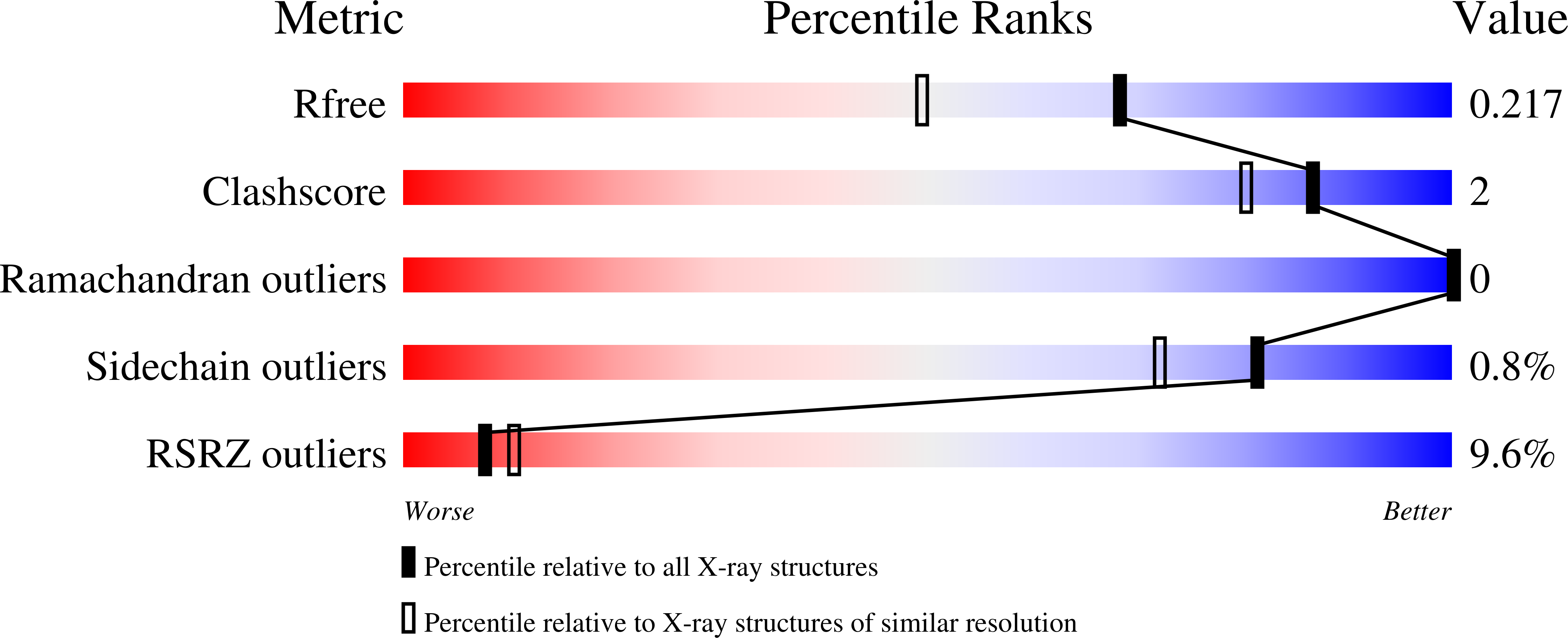
7L4V - PubMed Abstract:
DNA cytosine methylation in mammals modulates gene expression and chromatin accessibility. It also impacts mutation rates, via spontaneous oxidative deamination of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to thymine. In most cases the resulting T:G mismatches are repaired, following T excision by one of the thymine DNA glycosylases, TDG or MBD4. We found that C-to-T mutations are enriched in the binding sites of CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins (CEBP). Within a CEBP site, the presence of a T:G mismatch increased CEBPβ binding affinity by a factor of >60 relative to the normal C:G base pair. This enhanced binding to a mismatch inhibits its repair by both TDG and MBD4 in vitro. Furthermore, repair of the deamination product of unmethylated cytosine, which yields a U:G DNA mismatch that is normally repaired via uracil DNA glycosylase, is also inhibited by CEBPβ binding. Passage of a replication fork over either a T:G or U:G mismatch, before repair can occur, results in a C-to-T mutation in one of the daughter duplexes. Our study thus provides a plausible mechanism for accumulation of C-to-T human somatic mutations.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Epigenetics and Molecular Carcinogenesis, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX 77030, USA.