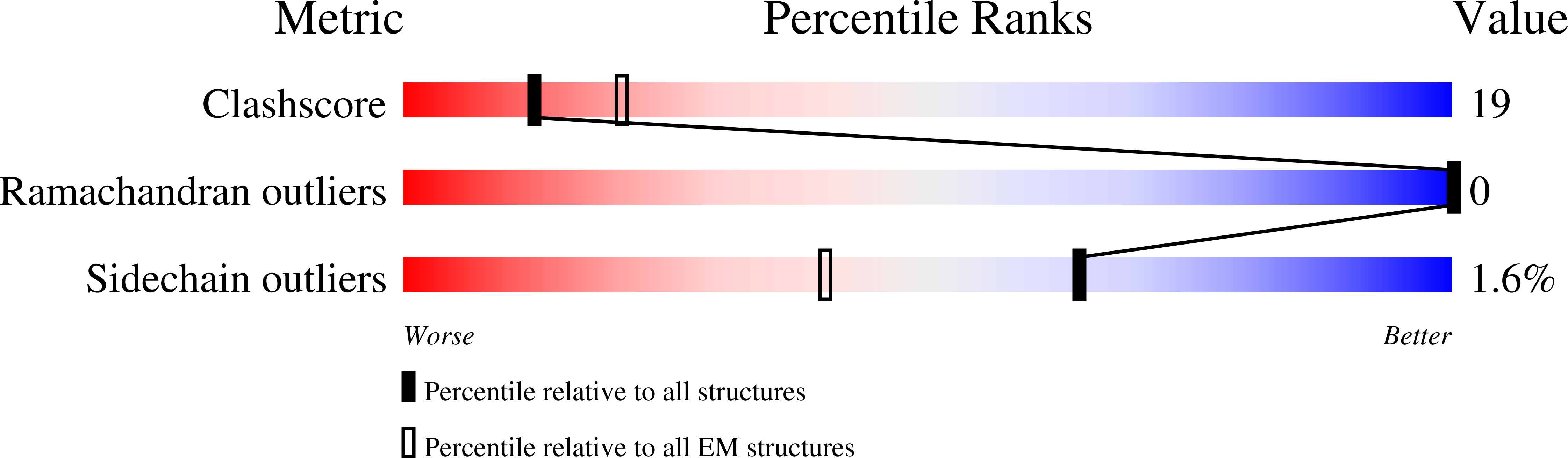Optical control of fast and processive engineered myosins in vitro and in living cells.
Ruijgrok, P.V., Ghosh, R.P., Zemsky, S., Nakamura, M., Gong, R., Ning, L., Chen, R., Vachharajani, V.T., Chu, A.E., Anand, N., Eguchi, R.R., Huang, P.S., Lin, M.Z., Alushin, G.M., Liphardt, J.T., Bryant, Z.(2021) Nat Chem Biol 17: 540-548
- PubMed: 33603247
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-021-00740-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
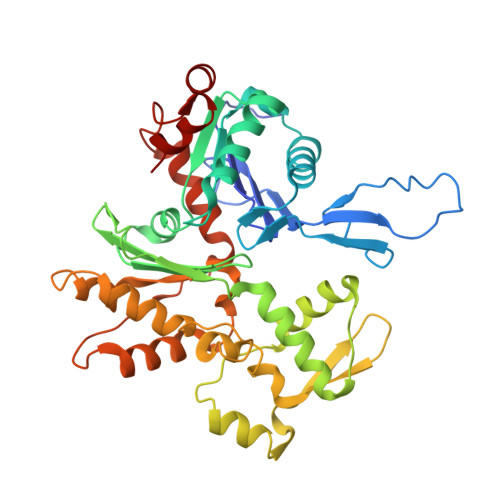
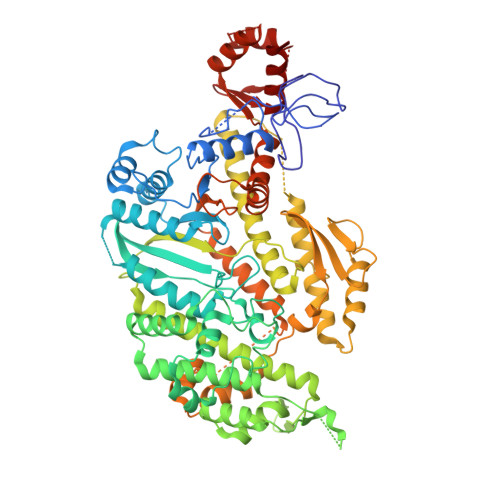
7KCH - PubMed Abstract:
Precision tools for spatiotemporal control of cytoskeletal motor function are needed to dissect fundamental biological processes ranging from intracellular transport to cell migration and division. Direct optical control of motor speed and direction is one promising approach, but it remains a challenge to engineer controllable motors with desirable properties such as the speed and processivity required for transport applications in living cells. Here, we develop engineered myosin motors that combine large optical modulation depths with high velocities, and create processive myosin motors with optically controllable directionality. We characterize the performance of the motors using in vitro motility assays, single-molecule tracking and live-cell imaging. Bidirectional processive motors move efficiently toward the tips of cellular protrusions in the presence of blue light, and can transport molecular cargo in cells. Robust gearshifting myosins will further enable programmable transport in contexts ranging from in vitro active matter reconstitutions to microfabricated systems that harness molecular propulsion.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bioengineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA.