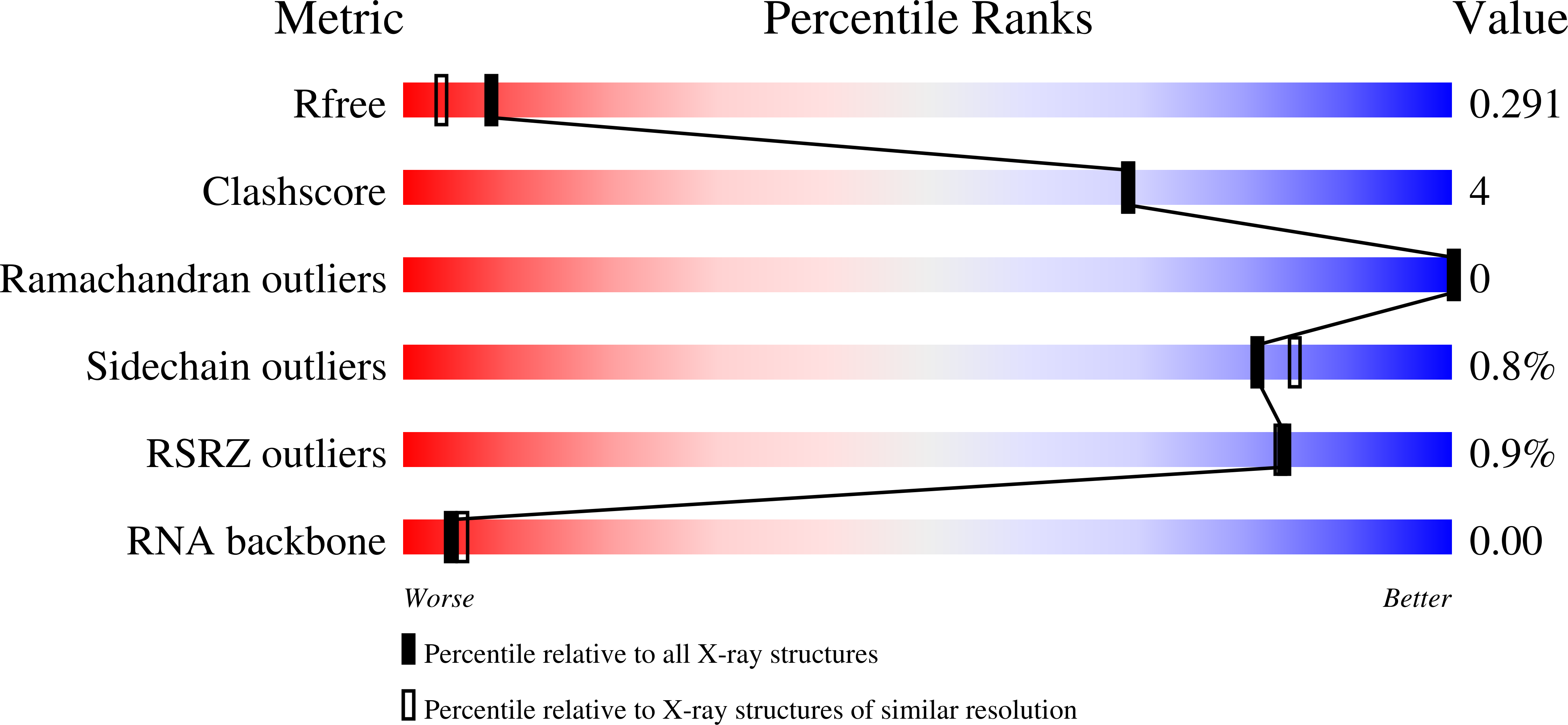
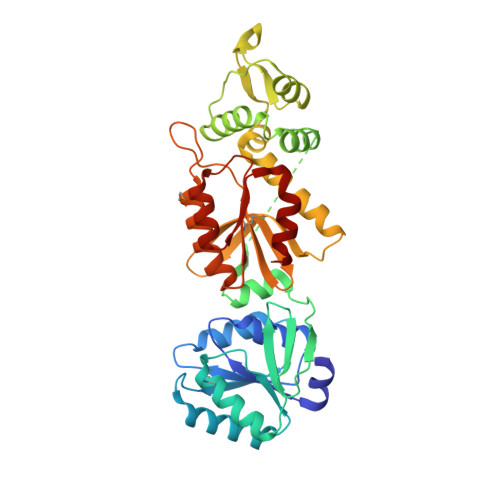
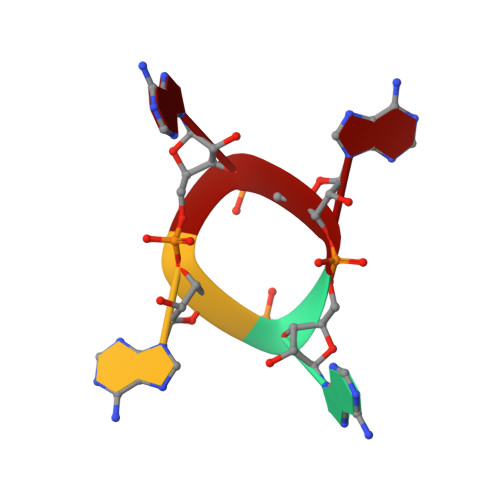
The CRISPR ancillary effector Can2 is a dual-specificity nuclease potentiating type III CRISPR defence.
Zhu, W., McQuarrie, S., Gruschow, S., McMahon, S.A., Graham, S., Gloster, T.M., White, M.F.(2021) Nucleic Acids Res 49: 2777-2789
- PubMed: 33590098
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab073
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7BDV - PubMed Abstract:
Cells and organisms have a wide range of mechanisms to defend against infection by viruses and other mobile genetic elements (MGE). Type III CRISPR systems detect foreign RNA and typically generate cyclic oligoadenylate (cOA) second messengers that bind to ancillary proteins with CARF (CRISPR associated Rossman fold) domains. This results in the activation of fused effector domains for antiviral defence. The best characterised CARF family effectors are the Csm6/Csx1 ribonucleases and DNA nickase Can1. Here we investigate a widely distributed CARF family effector with a nuclease domain, which we name Can2 (CRISPR ancillary nuclease 2). Can2 is activated by cyclic tetra-adenylate (cA4) and displays both DNase and RNase activity, providing effective immunity against plasmid transformation and bacteriophage infection in Escherichia coli. The structure of Can2 in complex with cA4 suggests a mechanism for the cA4-mediated activation of the enzyme, whereby an active site cleft is exposed on binding the activator. These findings extend our understanding of type III CRISPR cOA signalling and effector function.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biomedical Sciences Research Complex, School of Biology, University of St Andrews, St Andrews KY16 9ST, UK.