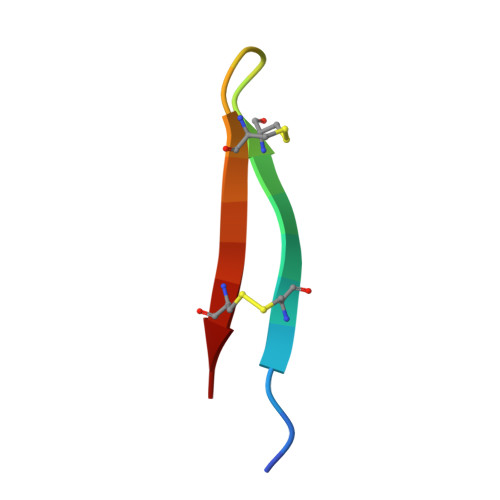
Structure Elucidation and Functional Studies of a Novel beta-hairpin Antimicrobial Peptide from the Marine Polychaeta Capitella teleta .
Panteleev, P.V., Tsarev, A.V., Safronova, V.N., Reznikova, O.V., Bolosov, I.A., Sychev, S.V., Shenkarev, Z.O., Ovchinnikova, T.V.(2020) Mar Drugs 18
- PubMed: 33291782
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/md18120620
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7ALD - PubMed Abstract:
Endogenous antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are evolutionary ancient molecular factors of innate immunity that play a key role in host defense. Among the most active and stable under physiological conditions AMPs are the peptides of animal origin that adopt a β-hairpin conformation stabilized by disulfide bridges. In this study, a novel BRICHOS-domain related AMP from the marine polychaeta Capitella teleta , named capitellacin, was produced as the recombinant analogue and investigated. The mature capitellacin exhibits high homology with the known β-hairpin AMP family-tachyplesins and polyphemusins from the horseshoe crabs. The β-hairpin structure of the recombinant capitellacin was proved by CD and NMR spectroscopy. In aqueous solution the peptide exists as monomeric right-handed twisted β-hairpin and its structure does not reveal significant amphipathicity. Moreover, the peptide retains this conformation in membrane environment and incorporates into lipid bilayer. Capitellacin exhibits a strong antimicrobial activity in vitro against a wide panel of bacteria including extensively drug-resistant strains. In contrast to other known β-hairpin AMPs, this peptide acts apparently via non-lytic mechanism at concentrations inhibiting bacterial growth. The molecular mechanism of the peptide antimicrobial action does not seem to be related to the inhibition of bacterial translation therefore other molecular targets may be assumed. The reduced cytotoxicity against human cells and high antibacterial cell selectivity as compared to tachyplesin-1 make it an attractive candidate compound for an anti-infective drug design.
Organizational Affiliation:
M.M. Shemyakin & Yu.A. Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, the Russian Academy of Sciences, Miklukho-Maklaya str., 16/10, 117997 Moscow, Russia.