An expandable, modular de novo protein platform for precision redox engineering.
Hutchins, G.H., Noble, C.E.M., Bunzel, H.A., Williams, C., Dubiel, P., Yadav, S.K.N., Molinaro, P.M., Barringer, R., Blackburn, H., Hardy, B.J., Parnell, A.E., Landau, C., Race, P.R., Oliver, T.A.A., Koder, R.L., Crump, M.P., Schaffitzel, C., Oliveira, A.S.F., Mulholland, A.J., Anderson, J.L.R.(2023) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 120: e2306046120-e2306046120
- PubMed: 37487099
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2306046120
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
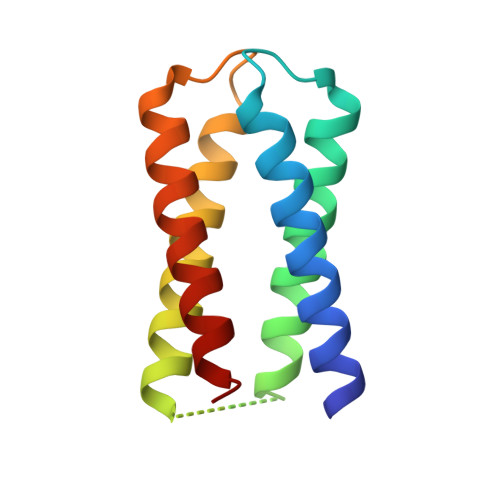
7AH0, 8CCR - PubMed Abstract:
The electron-conducting circuitry of life represents an as-yet untapped resource of exquisite, nanoscale biomolecular engineering. Here, we report the characterization and structure of a de novo diheme "maquette" protein, 4D2, which we subsequently use to create an expanded, modular platform for heme protein design. A well-folded monoheme variant was created by computational redesign, which was then utilized for the experimental validation of continuum electrostatic redox potential calculations. This demonstrates how fundamental biophysical properties can be predicted and fine-tuned. 4D2 was then extended into a tetraheme helical bundle, representing a 7 nm molecular wire. Despite a molecular weight of only 24 kDa, electron cryomicroscopy illustrated a remarkable level of detail, indicating the positioning of the secondary structure and the heme cofactors. This robust, expressible, highly thermostable and readily designable modular platform presents a valuable resource for redox protein design and the future construction of artificial electron-conducting circuitry.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biochemistry, University of Bristol, University Walk, Bristol BS8 1TD, United Kingdom.