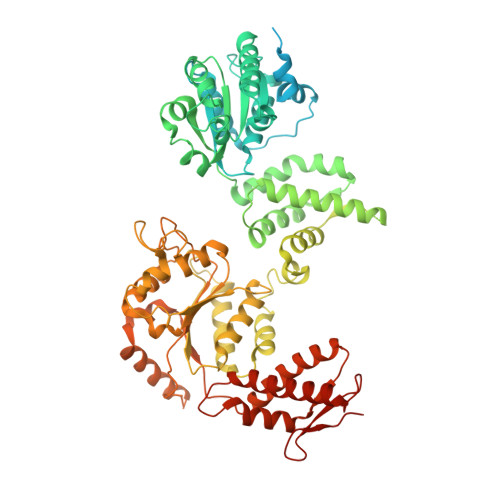
BacPROTACs mediate targeted protein degradation in bacteria.
Morreale, F.E., Kleine, S., Leodolter, J., Junker, S., Hoi, D.M., Ovchinnikov, S., Okun, A., Kley, J., Kurzbauer, R., Junk, L., Guha, S., Podlesainski, D., Kazmaier, U., Boehmelt, G., Weinstabl, H., Rumpel, K., Schmiedel, V.M., Hartl, M., Haselbach, D., Meinhart, A., Kaiser, M., Clausen, T.(2022) Cell 185: 2338
- PubMed: 35662409
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.05.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7AA4, 7ABR - PubMed Abstract:
Hijacking the cellular protein degradation system offers unique opportunities for drug discovery, as exemplified by proteolysis-targeting chimeras. Despite their great promise for medical chemistry, so far, it has not been possible to reprogram the bacterial degradation machinery to interfere with microbial infections. Here, we develop small-molecule degraders, so-called BacPROTACs, that bind to the substrate receptor of the ClpC:ClpP protease, priming neo-substrates for degradation. In addition to their targeting function, BacPROTACs activate ClpC, transforming the resting unfoldase into its functional state. The induced higher-order oligomer was visualized by cryo-EM analysis, providing a structural snapshot of activated ClpC unfolding a protein substrate. Finally, drug susceptibility and degradation assays performed in mycobacteria demonstrate in vivo activity of BacPROTACs, allowing selective targeting of endogenous proteins via fusion to an established degron. In addition to guiding antibiotic discovery, the BacPROTAC technology presents a versatile research tool enabling the inducible degradation of bacterial proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research Institute of Molecular Pathology, Vienna Biocenter, 1030 Vienna, Austria.