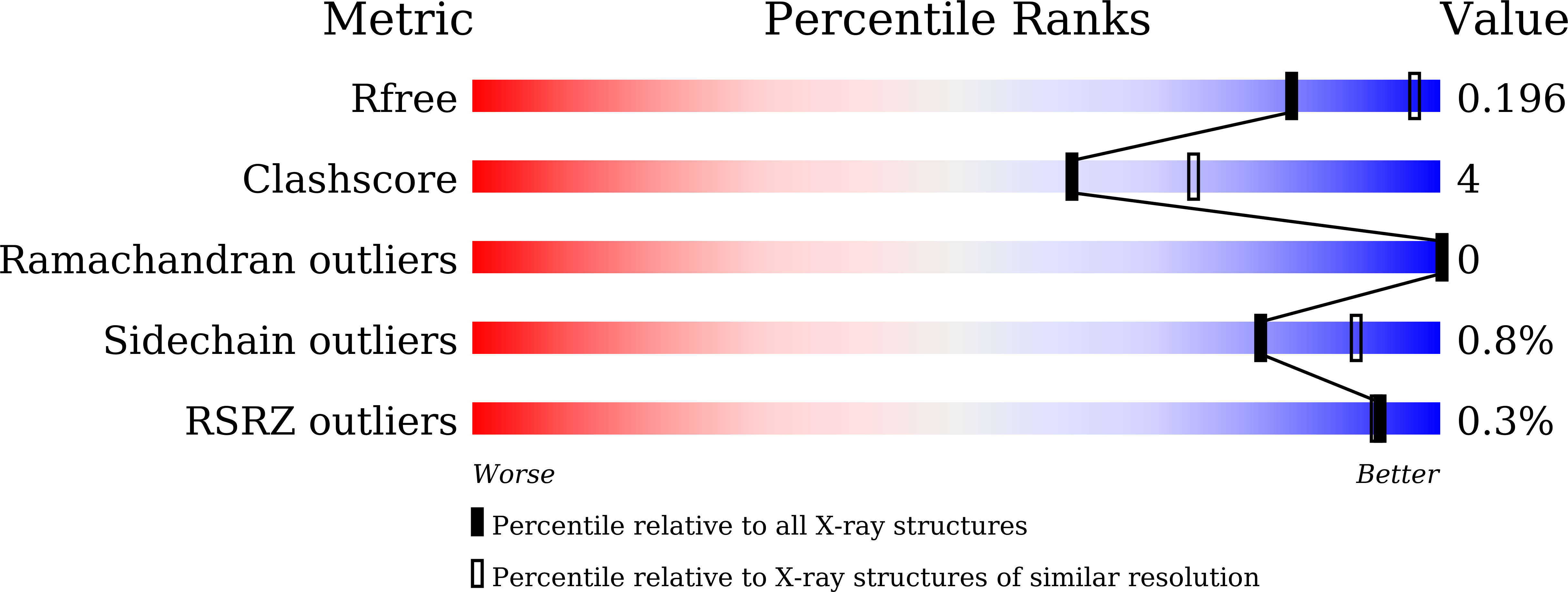
Lewis fucose is a key moiety for the recognition of histo-blood group antigens by GI.9 norovirus, as revealed by structural analysis.
Kimura-Someya, T., Kato-Murayama, M., Katsura, K., Sakai, N., Murayama, K., Hanada, K., Shirouzu, M., Someya, Y.(2022) FEBS Open Bio 12: 560-570
- PubMed: 35038379
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.13370
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7VP0, 7VS8, 7VS9 - PubMed Abstract:
Noroviruses have been identified as major causative agents of acute nonbacterial gastroenteritis in humans. Histo-blood group antigens (HBGAs) are thought to play a major role among the host cellular factors influencing norovirus infection. Genogroup I, genotype 9 (GI.9) is the most recently identified genotype within genogroup I, whose representative strain is the Vancouver 730 norovirus. However, the molecular interactions between host antigens and the GI.9 capsid protein have not been investigated in detail. In this study, we demonstrate that the GI.9 norovirus preferentially binds Lewis antigens over blood group A, B, and H antigens, as revealed by an HBGA binding assay using virus-like particles. We determined the crystal structures of the protruding domain of the GI.9 capsid protein in the presence or absence of Lewis antigens. Our analysis demonstrated that Lewis fucose (α1-3/4 fucose) represents a key moiety for the GI.9 protein-HBGA interaction, thus suggesting that Lewis antigens might play a critical role during norovirus infection. In addition to previously reported findings, our observations may support the future design of antiviral agents and vaccines against noroviruses.
Organizational Affiliation:
RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research, Yokohama, Japan.