HIC2 controls developmental hemoglobin switching by repressing BCL11A transcription.
Huang, P., Peslak, S.A., Ren, R., Khandros, E., Qin, K., Keller, C.A., Giardine, B., Bell, H.W., Lan, X., Sharma, M., Horton, J.R., Abdulmalik, O., Chou, S.T., Shi, J., Crossley, M., Hardison, R.C., Cheng, X., Blobel, G.A.(2022) Nat Genet 54: 1417-1426
- PubMed: 35941187
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-022-01152-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
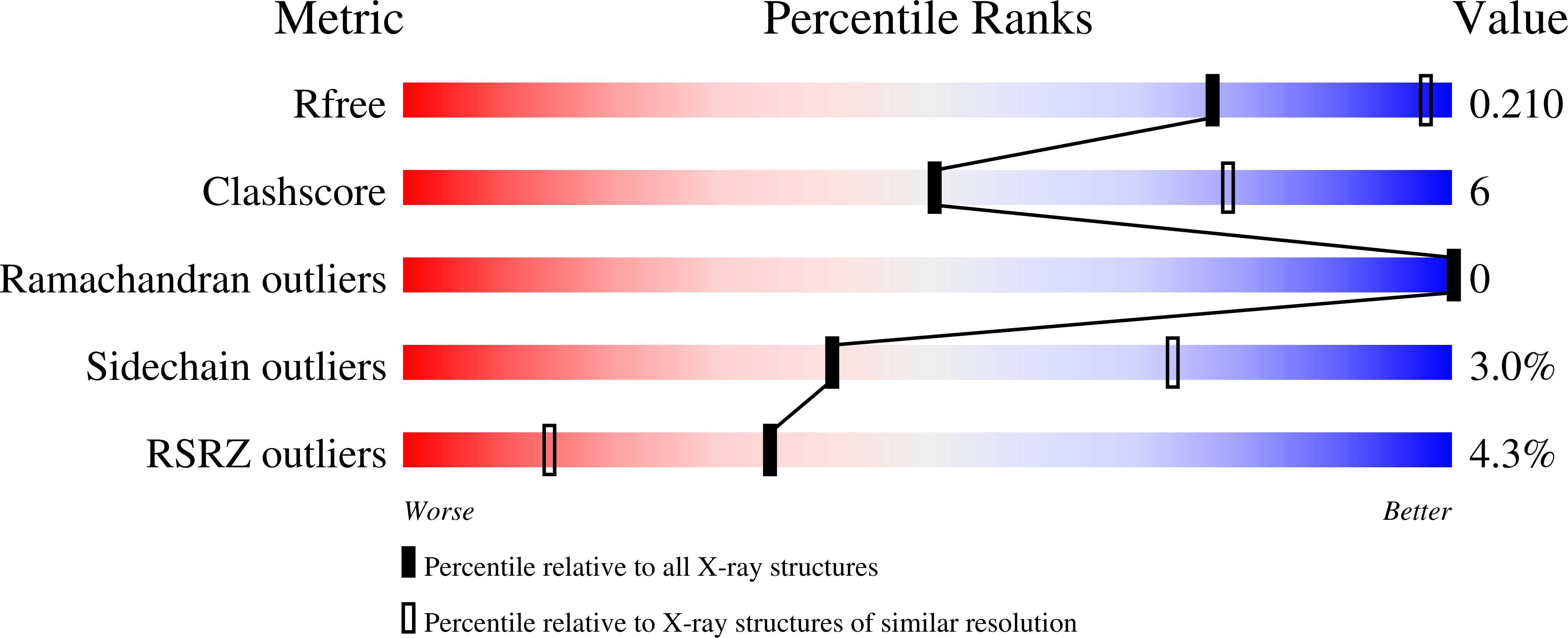
7TXC - PubMed Abstract:
The fetal-to-adult switch in hemoglobin production is a model of developmental gene control with relevance to the treatment of hemoglobinopathies. The expression of transcription factor BCL11A, which represses fetal β-type globin (HBG) genes in adult erythroid cells, is predominantly controlled at the transcriptional level but the underlying mechanism is unclear. We identify HIC2 as a repressor of BCL11A transcription. HIC2 and BCL11A are reciprocally expressed during development. Forced expression of HIC2 in adult erythroid cells inhibits BCL11A transcription and induces HBG expression. HIC2 binds to erythroid BCL11A enhancers to reduce chromatin accessibility and binding of transcription factor GATA1, diminishing enhancer activity and enhancer-promoter contacts. DNA-binding and crystallography studies reveal direct steric hindrance as one mechanism by which HIC2 inhibits GATA1 binding at a critical BCL11A enhancer. Conversely, loss of HIC2 in fetal erythroblasts increases enhancer accessibility, GATA1 binding and BCL11A transcription. HIC2 emerges as an evolutionarily conserved regulator of hemoglobin switching via developmental control of BCL11A.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Hematology, The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, USA. huangp1@chop.edu.