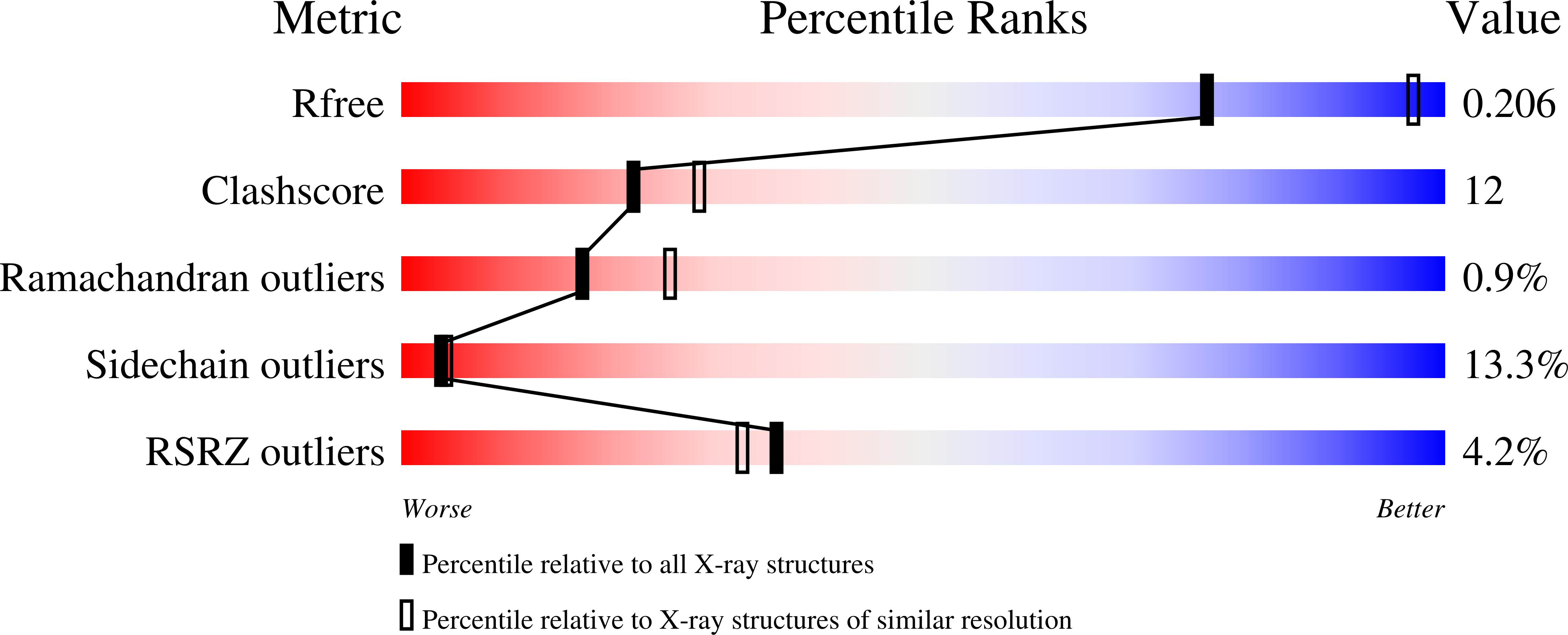
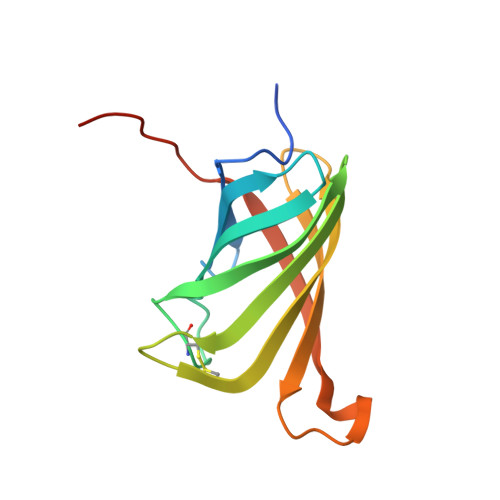
Wilavidin - a novel member of the avidin family that forms unique biotin-binding hexamers.
Avraham, O., Bayer, E.A., Livnah, O.(2022) FEBS J 289: 1700-1714
- PubMed: 34726340
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16259
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7OUQ, 7OUR, 7P8Y, 7P8Z - PubMed Abstract:
Nature's optimization of protein functions is a highly intricate evolutionary process. In addition to optimal tertiary folding, the intramolecular recognition among the monomers that generate higher-order quaternary arrangements is driven by stabilizing interactions that have a pivotal role for ideal activity. Homotetrameric avidin and streptavidin are regularly utilized in many applications, whereby their ultra-high affinity toward biotin is dependent on their quaternary arrangements. In recent years, a new subfamily of avidins was discovered that comprises homodimers rather than tetramers, in which the high affinity toward biotin is maintained. Intriguingly, several of the respective dimers have been shown to assemble into higher-order cylindrical hexamers or octamers that dissociate into dimers upon biotin binding. Here, we present wilavidin, a newly discovered member of the dimeric subfamily, forming hexamers in the apo form, which are uniquely maintained upon biotin binding with six high-affinity binding sites. Removal of the short C-terminal segment of wilavidin resulted in the presence of the dimer only, thus emphasizing the role of this segment in stabilizing the hexamer. Utilization of a hexavalent biotin-binding form of avidin would be beneficial for expanding the biotechnological toolbox. Additionally, this unique family of dimeric avidins and their propensity to oligomerize to hexamers or octamers can serve as a basis for protein oligomerization and intermonomeric recognition as well as cumulative interactions that determine molecular assemblies.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Wolfson Centre for Applied Structural Biology, Department of Biological Chemistry, Alexander Silverman Institute of Life Sciences, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel.