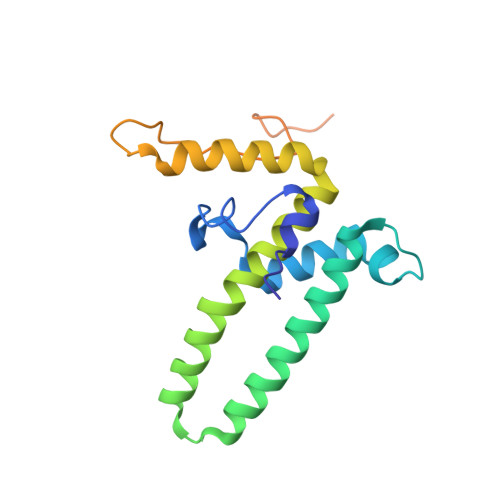
Conformational Plasticity of Hepatitis B Core Protein Spikes Promotes Peptide Binding Independent of the Secretion Phenotype.
Makbul, C., Khayenko, V., Maric, H.M., Bottcher, B.(2021) Microorganisms 9
- PubMed: 33946808
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9050956
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7OCO, 7OCW, 7OD4, 7OD6, 7OD7, 7OD8, 7OEN, 7OEV, 7OEW - PubMed Abstract:
Hepatitis B virus is a major human pathogen, which forms enveloped virus particles. During viral maturation, membrane-bound hepatitis B surface proteins package hepatitis B core protein capsids. This process is intercepted by certain peptides with an "LLGRMKG" motif that binds to the capsids at the tips of dimeric spikes. With microcalorimetry, electron cryo microscopy and peptide microarray-based screens, we have characterized the structural and thermodynamic properties of peptide binding to hepatitis B core protein capsids with different secretion phenotypes. The peptide "GSLLGRMKGA" binds weakly to hepatitis B core protein capsids and mutant capsids with a premature (F97L) or low-secretion phenotype (L60V and P5T). With electron cryo microscopy, we provide novel structures for L60V and P5T and demonstrate that binding occurs at the tips of the spikes at the dimer interface, splaying the helices apart independent of the secretion phenotype. Peptide array screening identifies "SLLGRM" as the core binding motif. This shortened motif binds only to one of the two spikes in the asymmetric unit of the capsid and induces a much smaller conformational change. Altogether, these comprehensive studies suggest that the tips of the spikes act as an autonomous binding platform that is unaffected by mutations that affect secretion phenotypes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Rudolf Virchow Center, Center for Integrative and Translational Bioimaging, University of Würzburg, 97080 Würzburg, Germany.