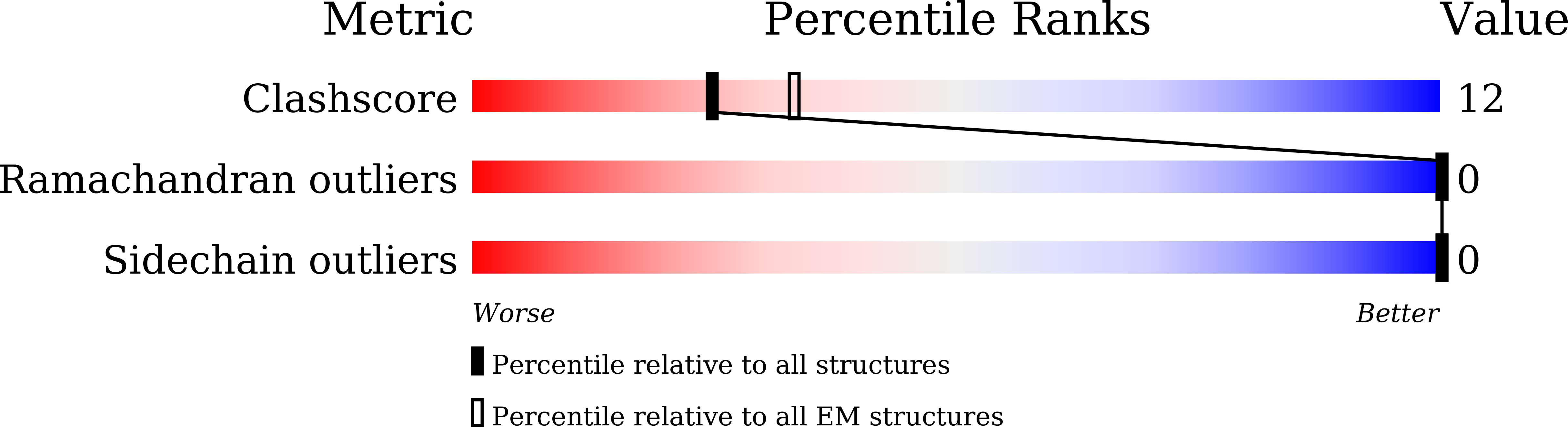Minimal protein-only RNase P structure reveals insights into tRNA precursor recognition and catalysis.
Teramoto, T., Koyasu, T., Adachi, N., Kawasaki, M., Moriya, T., Numata, T., Senda, T., Kakuta, Y.(2021) J Biol Chem 297: 101028-101028
- PubMed: 34339732
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101028
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7F3E - PubMed Abstract:
Ribonuclease P (RNase P) is an endoribonuclease that catalyzes the processing of the 5' leader sequence of precursor tRNA (pre-tRNA). Ribonucleoprotein RNase P and protein-only RNase P (PRORP) in eukaryotes have been extensively studied, but the mechanism by which a prokaryotic nuclease recognizes and cleaves pre-tRNA is unclear. To gain insights into this mechanism, we studied homologs of Aquifex RNase P (HARPs), thought to be enzymes of approximately 23 kDa comprising only this nuclease domain. We determined the cryo-EM structure of Aq880, the first identified HARP enzyme. The structure unexpectedly revealed that Aq880 consists of both the nuclease and protruding helical (PrH) domains. Aq880 monomers assemble into a dimer via the PrH domain. Six dimers form a dodecamer with a left-handed one-turn superhelical structure. The structure also revealed that the active site of Aq880 is analogous to that of eukaryotic PRORPs. The pre-tRNA docking model demonstrated that 5' processing of pre-tRNAs is achieved by two adjacent dimers within the dodecamer. One dimer is responsible for catalysis, and the PrH domains of the other dimer are responsible for pre-tRNA elbow recognition. Our study suggests that HARPs measure an invariant distance from the pre-tRNA elbow to cleave the 5' leader sequence, which is analogous to the mechanism of eukaryotic PRORPs and the ribonucleoprotein RNase P. Collectively, these findings shed light on how different types of RNase P enzymes utilize the same pre-tRNA processing.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Biophysical Chemistry, Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, Nishi-ku, Fukuoka, Japan. Electronic address: teramotot@agr.kyushu-u.ac.jp.