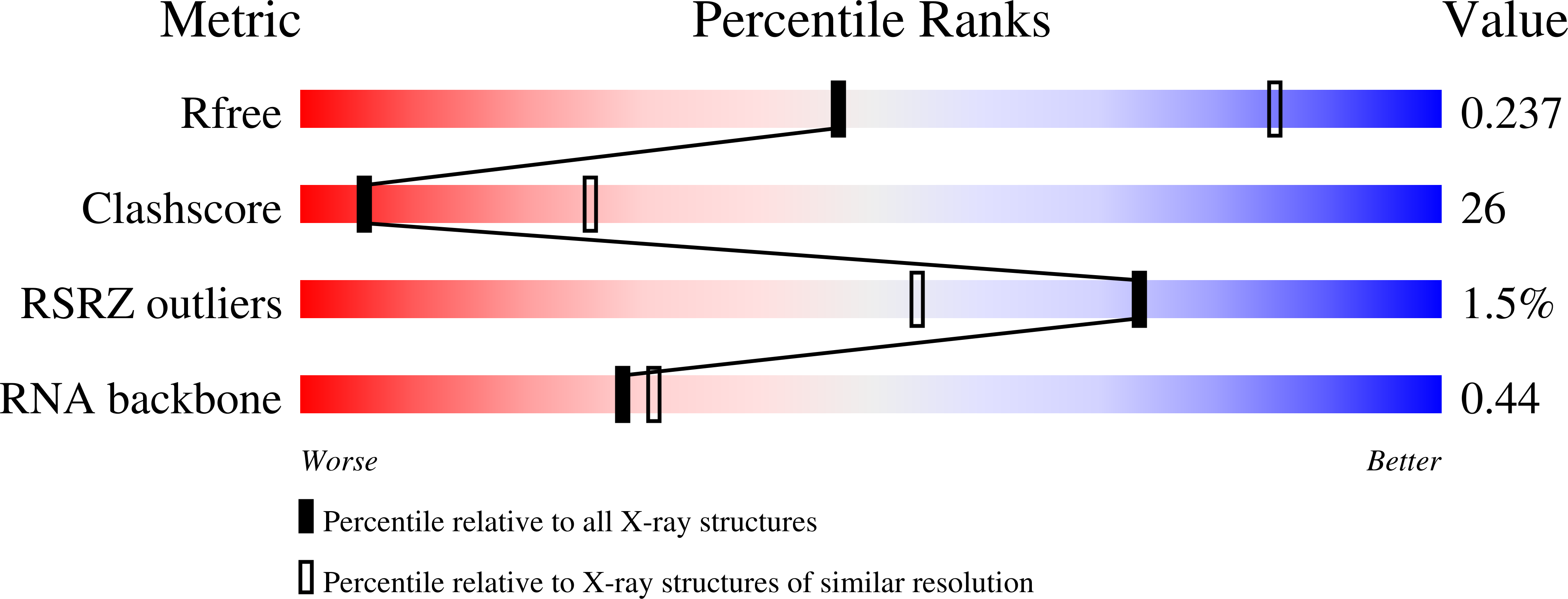Structural basis of the interaction between cyclodipeptide synthases and aminoacylated tRNA substrates.
Bourgeois, G., Seguin, J., Babin, M., Gondry, M., Mechulam, Y., Schmitt, E.(2020) RNA 26: 1589-1602
- PubMed: 32680846
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.075184.120
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6Y3G, 6Y4B - PubMed Abstract:
Cyclodipeptide synthases (CDPSs) catalyze the synthesis of various cyclodipeptides by using two aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) substrates in a sequential mechanism. Here, we studied binding of phenylalanyl-tRNA Phe to the CDPS from Candidatus Glomeribacter gigasporarum ( Cglo -CDPS) by gel filtration and electrophoretic mobility shift assay. We determined the crystal structure of the Cglo -CDPS:Phe-tRNA Phe complex to 5 Å resolution and further studied it in solution using small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). The data show that the major groove of the acceptor stem of the aa-tRNA interacts with the enzyme through the basic β2 and β7 strands of CDPSs belonging to the XYP subfamily. A bending of the CCA extremity enables the amino acid moiety to be positioned in the P1 pocket while the terminal A76 adenosine occupies the P2 pocket. Such a positioning indicates that the present structure illustrates the binding of the first aa-tRNA. In cells, CDPSs and the elongation factor EF-Tu share aminoacylated tRNAs as substrates. The present study shows that CDPSs and EF-Tu interact with opposite sides of tRNA. This may explain how CDPSs hijack aa-tRNAs from canonical ribosomal protein synthesis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratoire de Biologie Structurale de la Cellule, BIOC, Ecole polytechnique, CNRS, Institut Polytechnique de Paris, 91128 Palaiseau cedex, France.