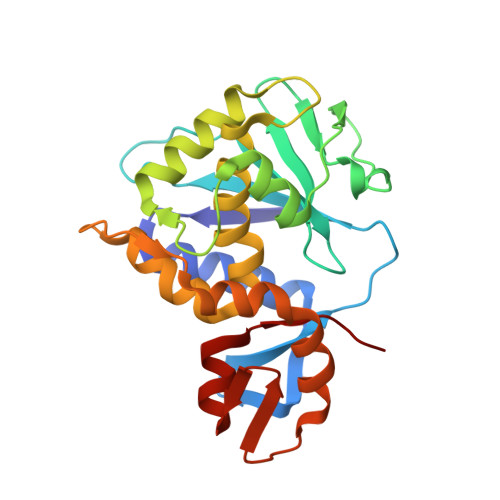
Structural basis for the interaction of Shiga toxin 2a with a C-terminal peptide of ribosomal P stalk proteins.
Rudolph, M.J., Davis, S.A., Tumer, N.E., Li, X.P.(2020) J Biol Chem 295: 15588-15596
- PubMed: 32878986
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.AC120.015070
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6X6H - PubMed Abstract:
The principal virulence factor of human pathogenic enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli is Shiga toxin (Stx). Shiga toxin 2a (Stx2a) is the subtype most commonly associated with severe disease outcomes such as hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. The catalytic A1 subunit (Stx2A1) binds to the conserved elongation factor binding C-terminal domain (CTD) of ribosomal P stalk proteins to inhibit translation. Stx2a holotoxin also binds to the CTD of P stalk proteins because the ribosome-binding site is exposed. We show here that Stx2a binds to an 11-mer peptide (P11) mimicking the CTD of P stalk proteins with low micromolar affinity. We cocrystallized Stx2a with P11 and defined their interactions by X-ray crystallography. We found that the last six residues of P11 inserted into a shallow pocket on Stx2A1 and interacted with Arg-172, Arg-176, and Arg-179, which were previously shown to be critical for binding of Stx2A1 to the ribosome. Stx2a formed a distinct P11-binding mode within a different surface pocket relative to ricin toxin A subunit and trichosanthin, suggesting different ribosome recognition mechanisms for each ribosome inactivating protein (RIP). The binding mode of Stx2a to P11 is also conserved among the different Stx subtypes. Furthermore, the P stalk protein CTD is flexible and adopts distinct orientations and interaction modes depending on the structural differences between the RIPs. Structural characterization of the Stx2a-ribosome complex is important for understanding the role of the stalk in toxin recruitment to the sarcin/ricin loop and may provide a new target for inhibitor discovery.
Organizational Affiliation:
New York Structural Biology Center, New York, New York, USA.