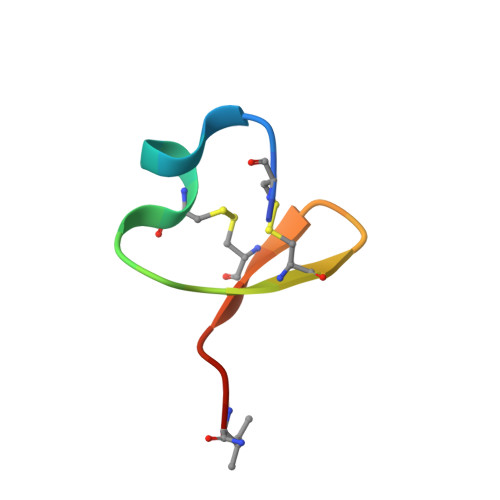
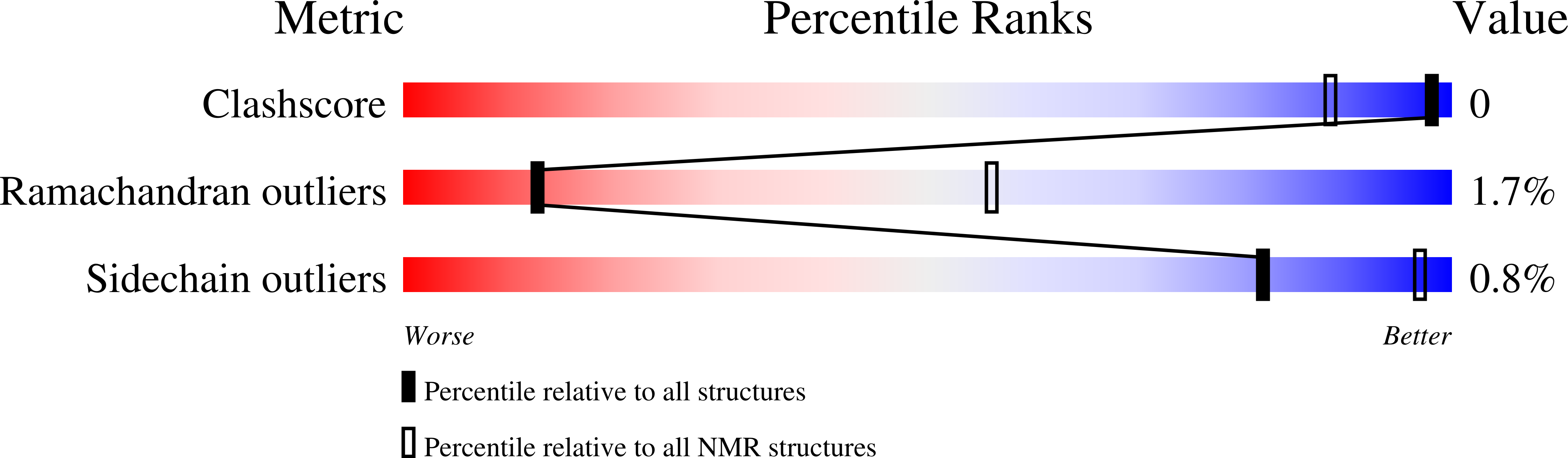Pharmacological activity and NMR solution structure of the leech peptide HSTX-I.
McMahon, K.L., Tay, B., Deuis, J.R., Tanaka, B.S., Peigneur, S., Jin, A.H., Tytgat, J., Waxman, S.G., Dib-Hajj, S.D., Vetter, I., Schroeder, C.I.(2020) Biochem Pharmacol 181: 114082-114082
- PubMed: 32524995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114082
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6WQR - PubMed Abstract:
The role of voltage-gated sodium (Na V ) channels in pain perception is indisputable. Of particular interest as targets for the development of pain therapeutics are the tetrodotoxin-resistant isoforms Na V 1.8 and Na V 1.9, based on animal as well as human genetic studies linking these ion channel subtypes to the pathogenesis of pain. However, only a limited number of inhibitors selectively targeting these channels have been reported. HSTX-I is a peptide toxin identified from saliva of the leech Haemadipsa sylvestris. The native 23-residue peptide, stabilised by two disulfide bonds, has been reported to inhibit rat Na V 1.8 and mouse Na V 1.9 with low micromolar activity, and may therefore represent a scaffold for development of novel modulators with activity at human tetrodotoxin-resistant Na V isoforms. We synthetically produced this hydrophobic peptide in high yield using a one-pot oxidation and single step purification and determined the three-dimensional solution structure of HSTX-I using NMR solution spectroscopy. However, in our hands, the synthetic HSTX-I displayed only very modest activity at human Na V 1.8 and Na V 1.9, and lacked analgesic efficacy in a murine model of inflammatory pain.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Queensland 4072, Australia.