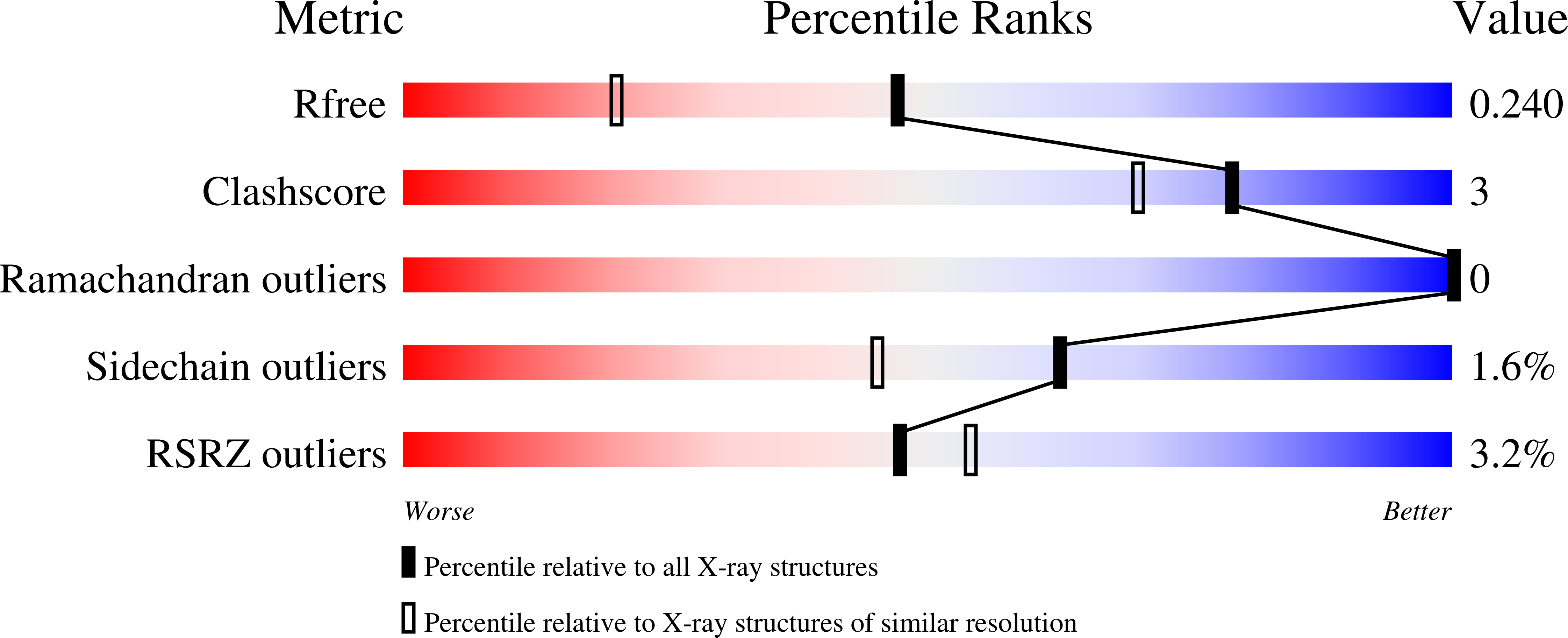
Structural Basis for the Regulation of Biofilm Formation and Iron Uptake in A. baumannii by the Blue-Light-Using Photoreceptor, BlsA.
Chitrakar, I., Iuliano, J.N., He, Y., Woroniecka, H.A., Tolentino Collado, J., Wint, J.M., Walker, S.G., Tonge, P.J., French, J.B.(2020) ACS Infect Dis 6: 2592-2603
- PubMed: 32926768
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00156
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6W6Z, 6W72 - PubMed Abstract:
The opportunistic human pathogen, A. baumannii , senses and responds to light using the blue light sensing A (BlsA) photoreceptor protein. BlsA is a blue-light-using flavin adenine dinucleotide (BLUF) protein that is known to regulate a wide variety of cellular functions through interactions with different binding partners. Using immunoprecipitation of tagged BlsA in A. baumannii lysates, we observed a number of proteins that interact with BlsA, including several transcription factors. In addition to a known binding partner, the iron uptake regulator Fur, we identified the biofilm response regulator BfmR as a putative BlsA-binding partner. Using microscale thermophoresis, we determined that both BfmR and Fur bind to BlsA with nanomolar binding constants. To better understand how BlsA interacts with and regulates these transcription factors, we solved the X-ray crystal structures of BlsA in both a ground (dark) state and a photoactivated light state. Comparison of the light- and dark-state structures revealed that, upon photoactivation, the two α-helices comprising the variable domain of BlsA undergo a distinct conformational change. The flavin-binding site, however, remains largely unchanged from dark to light. These structures, along with docking studies of BlsA and Fur, reveal key mechanistic details about how BlsA propagates the photoactivation signal between protein domains and on to its binding partner. Taken together, our structural and biophysical data provide important insights into how BlsA controls signal transduction in A. baumannii and provides a likely mechanism for blue-light-dependent modulation of biofilm formation and iron uptake.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, Austin, Minnesota 55912, United States.