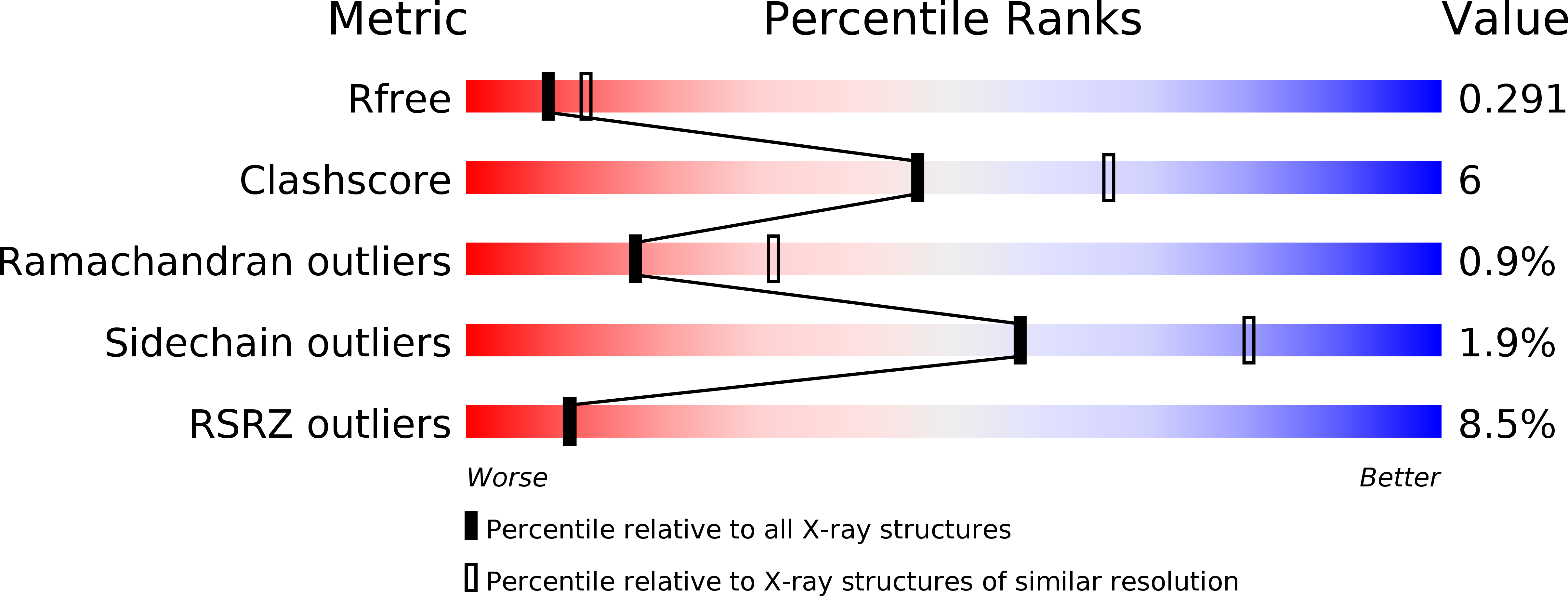
An enumerative algorithm for de novo design of proteins with diverse pocket structures.
Basanta, B., Bick, M.J., Bera, A.K., Norn, C., Chow, C.M., Carter, L.P., Goreshnik, I., Dimaio, F., Baker, D.(2020) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117: 22135-22145
- PubMed: 32839327
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2005412117
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6W3D, 6W3F, 6W3G, 6W3W, 6W40 - PubMed Abstract:
To create new enzymes and biosensors from scratch, precise control over the structure of small-molecule binding sites is of paramount importance, but systematically designing arbitrary protein pocket shapes and sizes remains an outstanding challenge. Using the NTF2-like structural superfamily as a model system, we developed an enumerative algorithm for creating a virtually unlimited number of de novo proteins supporting diverse pocket structures. The enumerative algorithm was tested and refined through feedback from two rounds of large-scale experimental testing, involving in total the assembly of synthetic genes encoding 7,896 designs and assessment of their stability on yeast cell surface, detailed biophysical characterization of 64 designs, and crystal structures of 5 designs. The refined algorithm generates proteins that remain folded at high temperatures and exhibit more pocket diversity than naturally occurring NTF2-like proteins. We expect this approach to transform the design of small-molecule sensors and enzymes by enabling the creation of binding and active site geometries much more optimal for specific design challenges than is accessible by repurposing the limited number of naturally occurring NTF2-like proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Protein Design, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195.