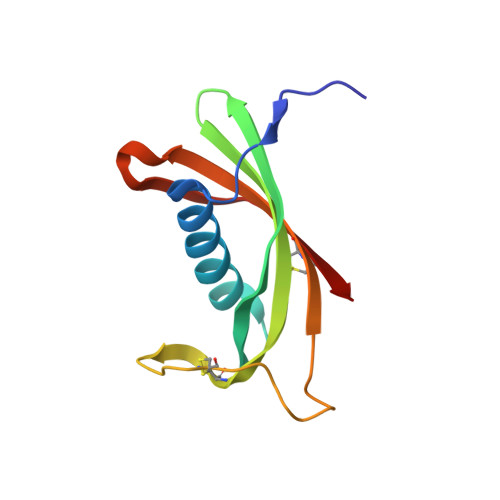
Maturation of the functional mouse CRES amyloid from globular form.
Hewetson, A., Khan, N.H., Dominguez, M.J., Do, H.Q., Kusko, R.E., Borcik, C.G., Rigden, D.J., Keegan, R.M., Sutton, R.B., Latham, M.P., Wylie, B.J., Cornwall, G.A.(2020) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117: 16363-16372
- PubMed: 32601205
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2006887117
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
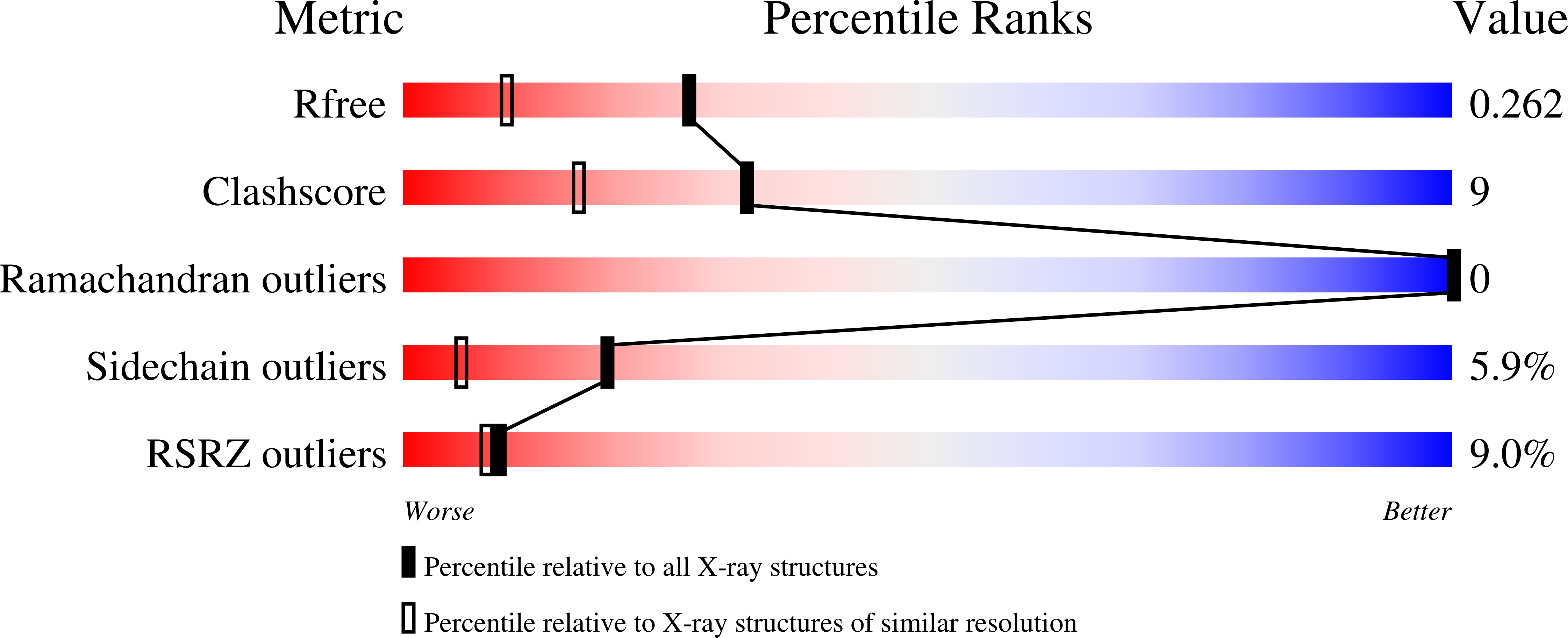
6UIO - PubMed Abstract:
The epididymal lumen contains a complex cystatin-rich nonpathological amyloid matrix with putative roles in sperm maturation and sperm protection. Given our growing understanding for the biological function of this and other functional amyloids, the problem still remains: how functional amyloids assemble including their initial transition to early oligomeric forms. To examine this, we developed a protocol for the purification of nondenatured mouse CRES, a component of the epididymal amyloid matrix, allowing us to examine its assembly to amyloid under conditions that may mimic those in vivo. Herein we use X-ray crystallography, solution-state NMR, and solid-state NMR to follow at the atomic level the assembly of the CRES amyloidogenic precursor as it progressed from monomeric folded protein to an advanced amyloid. We show the CRES monomer has a typical cystatin fold that assembles into highly branched amyloid matrices, comparable to those in vivo, by forming β-sheet assemblies that our data suggest occur via two distinct mechanisms: a unique conformational switch of a highly flexible disulfide-anchored loop to a rigid β-strand and by traditional cystatin domain swapping. Our results provide key insight into our understanding of functional amyloid assembly by revealing the earliest structural transitions from monomer to oligomer and by showing that some functional amyloid structures may be built by multiple and distinctive assembly mechanisms.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cell Biology and Biochemistry, Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Lubbock, TX 79430.