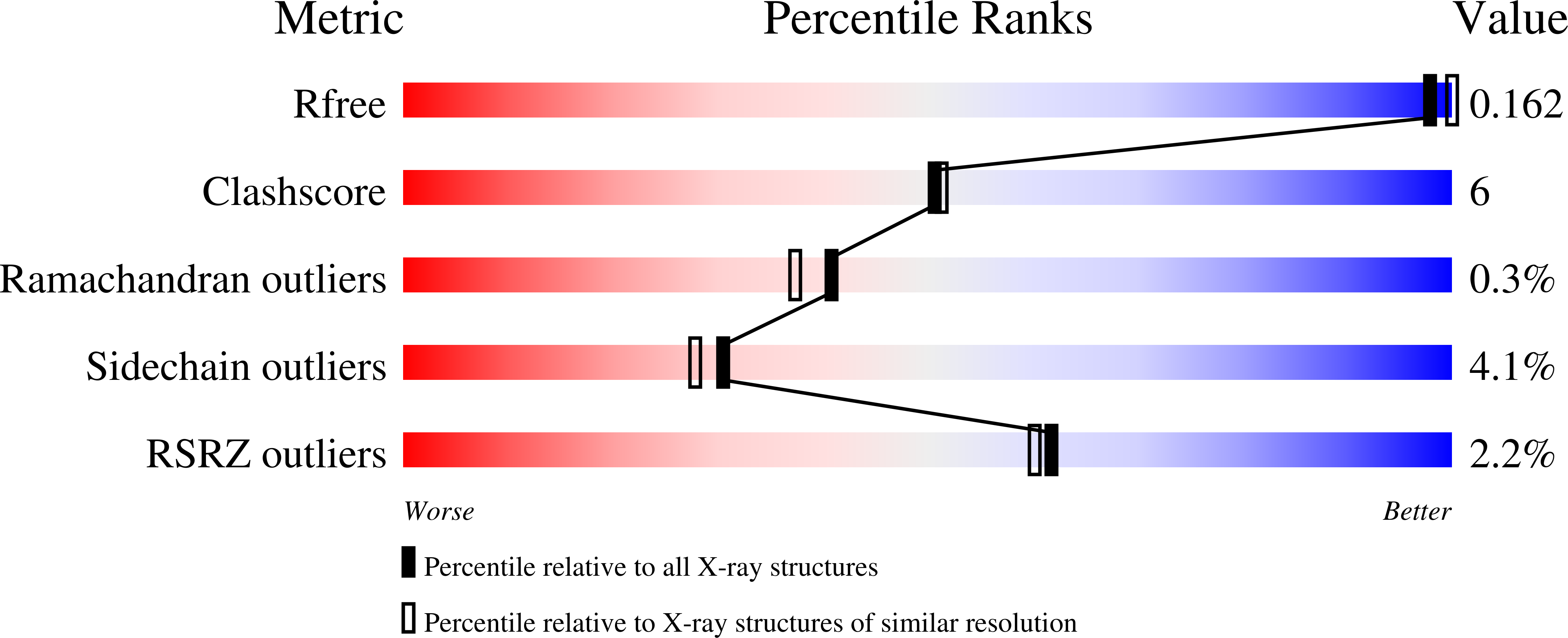
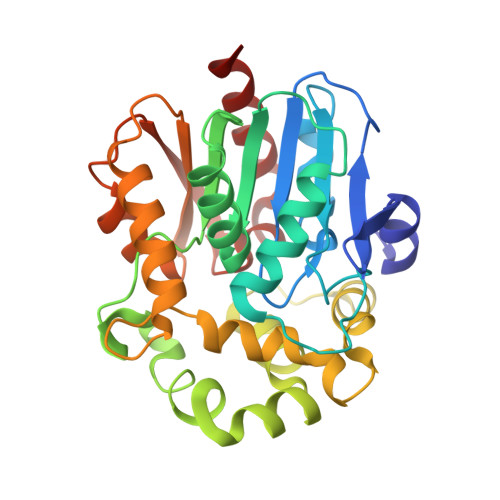
Engineering the protein dynamics of an ancestral luciferase.
Schenkmayerova, A., Pinto, G.P., Toul, M., Marek, M., Hernychova, L., Planas-Iglesias, J., Daniel Liskova, V., Pluskal, D., Vasina, M., Emond, S., Dorr, M., Chaloupkova, R., Bednar, D., Prokop, Z., Hollfelder, F., Bornscheuer, U.T., Damborsky, J.(2021) Nat Commun 12: 3616-3616
- PubMed: 34127663
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23450-z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6S6E, 6S97, 6YN2 - PubMed Abstract:
Protein dynamics are often invoked in explanations of enzyme catalysis, but their design has proven elusive. Here we track the role of dynamics in evolution, starting from the evolvable and thermostable ancestral protein Anc HLD-RLuc which catalyses both dehalogenase and luciferase reactions. Insertion-deletion (InDel) backbone mutagenesis of Anc HLD-RLuc challenged the scaffold dynamics. Screening for both activities reveals InDel mutations localized in three distinct regions that lead to altered protein dynamics (based on crystallographic B-factors, hydrogen exchange, and molecular dynamics simulations). An anisotropic network model highlights the importance of the conformational flexibility of a loop-helix fragment of Renilla luciferases for ligand binding. Transplantation of this dynamic fragment leads to lower product inhibition and highly stable glow-type bioluminescence. The success of our approach suggests that a strategy comprising (i) constructing a stable and evolvable template, (ii) mapping functional regions by backbone mutagenesis, and (iii) transplantation of dynamic features, can lead to functionally innovative proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
International Clinical Research Center, St. Anne's University Hospital Brno, Brno, Czech Republic.