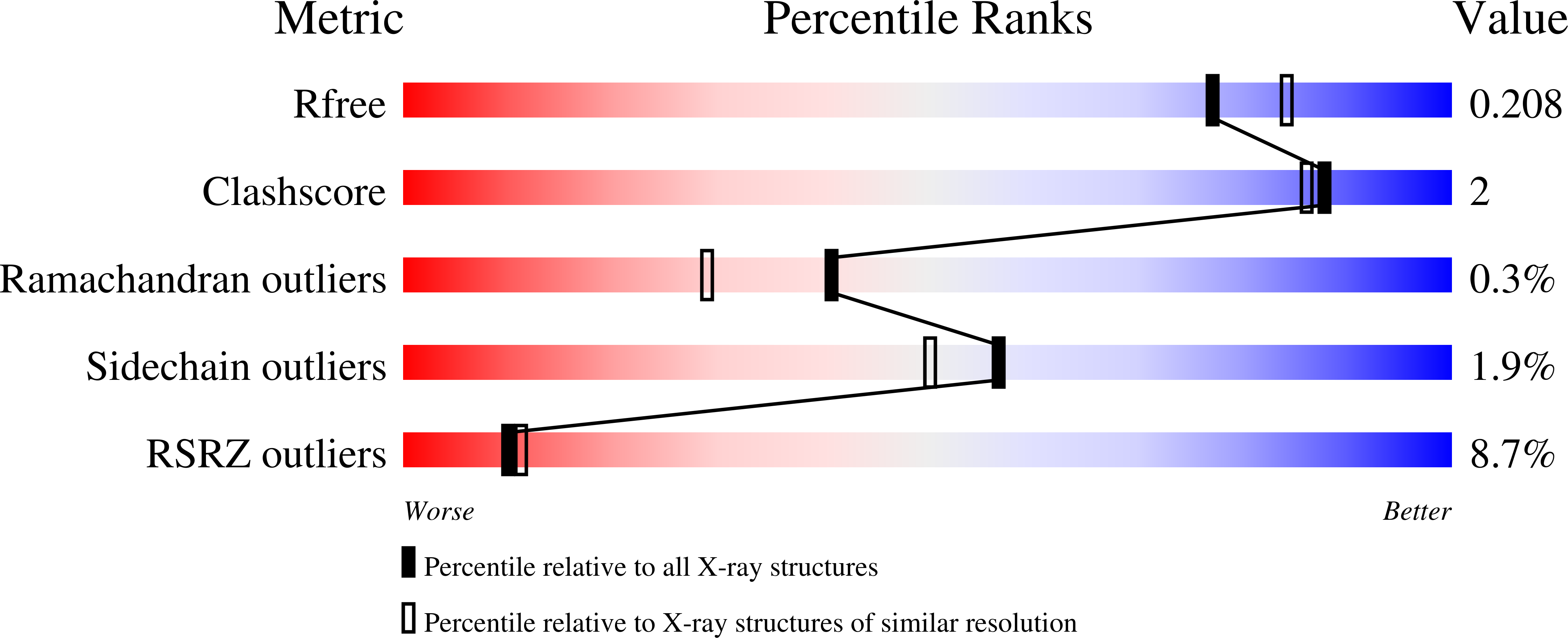
Alternative conformation of the C-domain of the P140 protein from Mycoplasma genitalium.
Vizarraga, D., Perez-Luque, R., Martin, J., Fita, I., Aparicio, D.(2020) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 76: 508-516
- PubMed: 33135669
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X20012297
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6RCC, 6RCD - PubMed Abstract:
The human pathogen Mycoplasma genitalium is responsible for urethritis in men, and for cervicitis and pelvic inflammatory disease in women. The adherence of M. genitalium to host target epithelial cells is mediated through an adhesion complex called Nap, which is essential for infectivity. Nap is a transmembrane dimer of heterodimers of the immunodominant proteins P110 and P140. The M. genitalium genome contains multiple copies of portions that share homology with the extracellular regions of P140 and P110 encoded by the genes mg191 and mg192, respectively. Homologous recombination between the genes and the copies allows the generation of a large diversity of P140 and P110 variants to overcome surveillance by the host immune system. Interestingly, the C-terminal domain (C-domain) of the extracellular region of P140, which is essential for the function of Nap by acting as a flexible stalk anchoring the protein to the mycoplasma membrane, presents a low degree of sequence variability. In the present work, the X-ray crystal structures of two crystal forms of a construct of the P140 C-domain are reported. In both crystal forms, the construct forms a compact octamer with D4 point-group symmetry. The structure of the C-domain determined in this work presents significant differences with respect to the structure of the C-domain found recently in intact P140. The structural plasticity of the C-domain appears to be a possible mechanism that may help in the functioning of the mycoplasma adhesion complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, Institut de Biologia Molecular de Barcelona (IBMB-CSIC), Parc Científic de Barcelona, Baldiri Reixac 10-12, 08028 Barcelona, Spain.