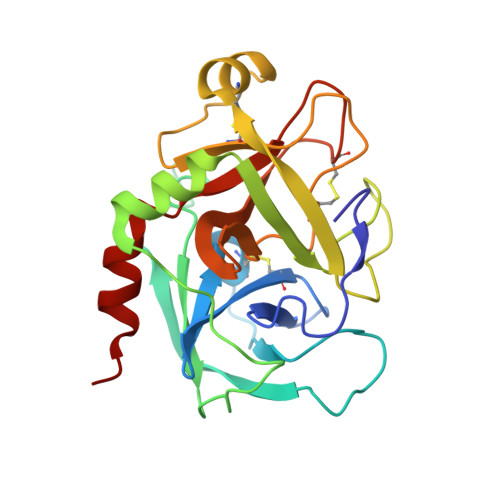
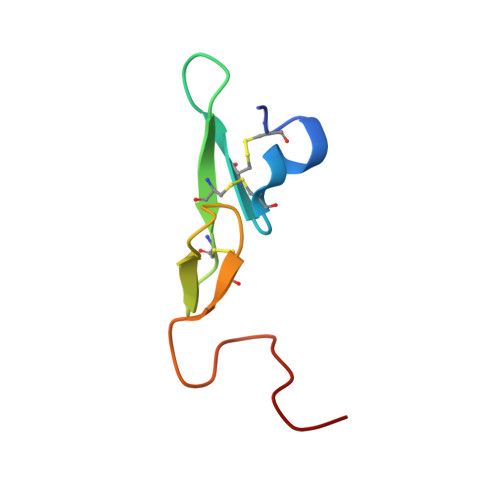
Sodium-site in serine protease domain of human coagulation factor IXa: evidence from the crystal structure and molecular dynamics simulations study.
Vadivel, K., Schreuder, H.A., Liesum, A., Schmidt, A.E., Goldsmith, G., Bajaj, S.P.(2019) J Thromb Haemost 17: 574-584
- PubMed: 30725510
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.14401
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6MV4 - PubMed Abstract:
Essentials Consensus sequence and biochemical data suggest a Na + -site in the factor (F) IXa protease domain. X-ray structure of the FIXa EGF2/protease domain at 1.37 Å reveals a Na + -site not observed earlier. Molecular dynamics simulations data support that Na + ± Ca 2+ promote FIXa protease domain stability. Sulfate ions found in the protease domain mimic heparin sulfate binding mode in FIXa. SUMMARY: Background Activated coagulation factor IX (FIXa) consists of a γ-carboxyglutamic acid domain, two epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) domains, and a C-terminal protease domain. Consensus sequence and biochemical data support the existence of a Na + -site in the FIXa protease domain. However, soaking experiments or crystals grown in high concentration of ammonium sulfate did not reveal a Na + -site in wild-type or mutant FIXa EGF2/protease domain structure. Objective Determine the structure of the FIXa EGF2/protease domain in the presence of Na + ; perform molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to explore the role of Na + in stabilizing FIXa structure. Methods Crystallography, MD simulations, and modeling heparin binding to FIXa. Results Crystal structure at 1.37-Å resolution revealed that Na + is coordinated to carbonyl groups of residues 184A, 185, 221A, and 224 in the FIXa protease domain. The Na + -site in FIXa is similar to that of FXa and is linked to the Asp189 S1-site. In MD simulations, Na + reduced fluctuations in residues 217-225 (Na + -loop) and 70-80 (Ca 2+ -loop), whereas Ca 2+ reduced fluctuations only in residues of the Ca 2+ -loop. Ca 2+ and Na + together reduced fluctuations in residues of the Ca 2+ -loop and Na + -loop (residues 70-80, 183-194, and 217-225). Moreover, we observed four sulfate ions that make salt bridges with FIXa protease domain Arg/Lys residues, which have been implicated in heparin binding. Based upon locations of the sulfate ions, we modeled heparin binding to FIXa, which is similar to the heparin binding in thrombin. Conclusions The FIXa Na + -site in association with Ca 2+ contributes to stabilization of the FIXa protease domain. The heparin binding mode in FIXa is similar to that in thrombin.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA.