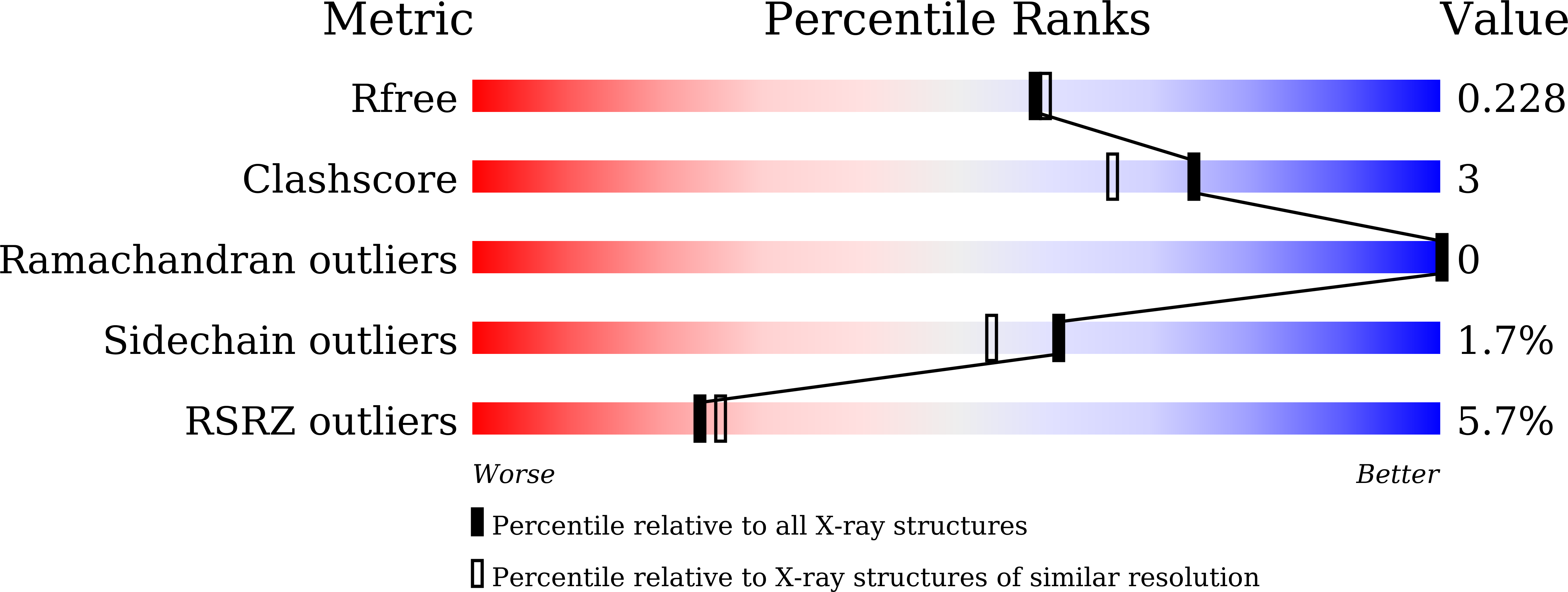
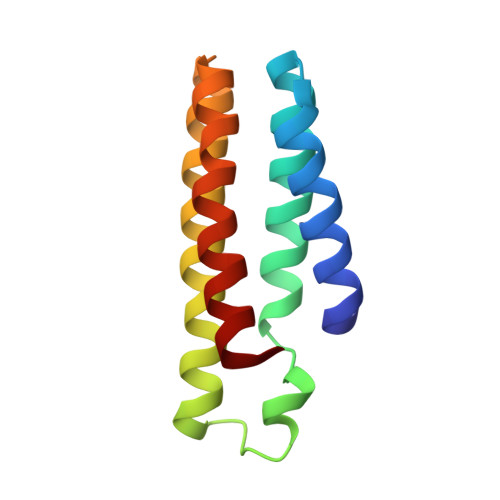
Symmetry-related residues as promising hotspots for the evolution of de novo oligomeric enzymes.
Yu, J., Yang, J., Seok, C., Song, W.J.(2021) Chem Sci 12: 5091-5101
- PubMed: 34168770
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d0sc06823c
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LDE, 6LDF, 6LDG, 7DCL - PubMed Abstract:
Directed evolution has provided us with great opportunities and prospects in the synthesis of tailor-made proteins. It, however, often requires at least mid to high throughput screening, necessitating more effective strategies for laboratory evolution. We herein demonstrate that protein symmetry can be a versatile criterion for searching for promising hotspots for the directed evolution of de novo oligomeric enzymes. The randomization of symmetry-related residues located at the rotational axes of artificial metallo-β-lactamase yields drastic effects on catalytic activities, whereas that of non-symmetry-related, yet, proximal residues to the active site results in negligible perturbations. Structural and biochemical analysis of the positive hits indicates that seemingly trivial mutations at symmetry-related spots yield significant alterations in overall structures, metal-coordination geometry, and chemical environments of active sites. Our work implicates that numerous artificially designed and natural oligomeric proteins might have evolutionary advantages of propagating beneficial mutations using their global symmetry.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, College of Natural Sciences, Seoul National University Seoul 08826 Republic of Korea woonjusong@snu.ac.kr.