Structural insights into the interaction between phytoplasmal effector causing phyllody 1 and MADS transcription factors.
Liao, Y.T., Lin, S.S., Lin, S.J., Sun, W.T., Shen, B.N., Cheng, H.P., Lin, C.P., Ko, T.P., Chen, Y.F., Wang, H.C.(2019) Plant J 100: 706-719
- PubMed: 31323156
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14463
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
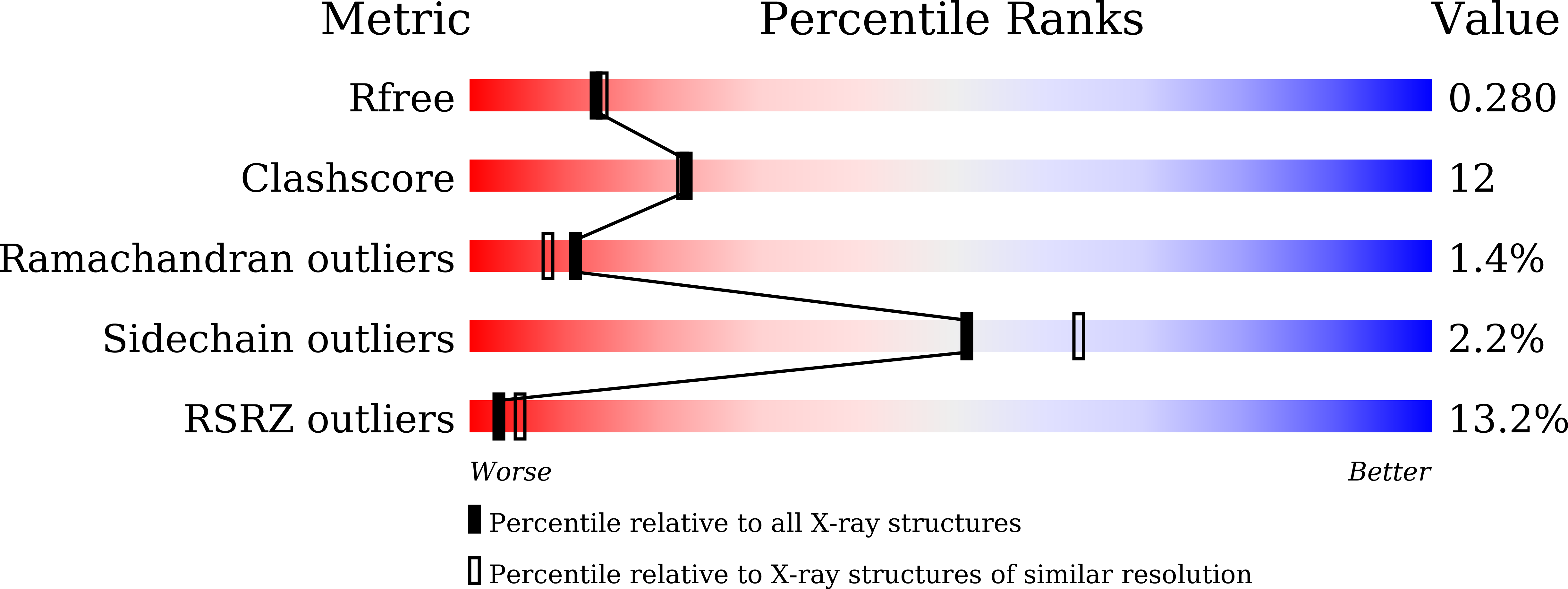
6INR - PubMed Abstract:
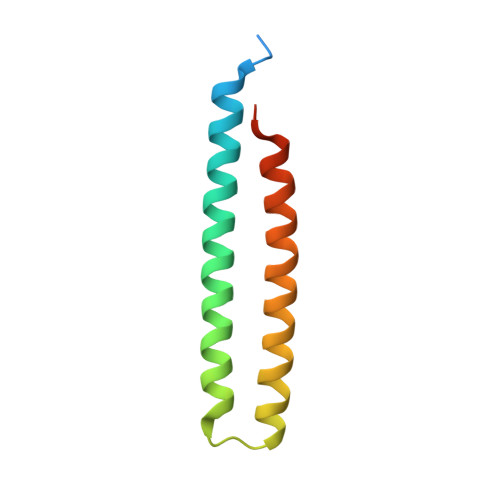
Phytoplasmas are bacterial plant pathogens which can induce severe symptoms including dwarfism, phyllody and virescence in an infected plant. Because phytoplasmas infect many important crops such as peanut and papaya they have caused serious agricultural losses. The phytoplasmal effector causing phyllody 1 (PHYL1) is an important phytoplasmal pathogenic factor which affects the biological function of MADS transcription factors by interacting with their K (keratin-like) domain, thus resulting in abnormal plant developments such as phyllody. Until now, lack of information on the structure of PHYL1 has prevented a detailed understanding of the binding mechanism between PHYL1 and the MADS transcription factors. Here, we present the crystal structure of PHYL1 from peanut witches'-broom phytoplasma (PHYL1 Pn WB ). This protein was found to fold into a unique α-helical hairpin with exposed hydrophobic residues on its surface that may play an important role in its biological function. Using proteomics approaches, we propose a binding mode of PHYL1 Pn WB with the K domain of the MADS transcription factor SEPALLATA3 (SEP3_K) and identify the residues of PHYL1 Pn WB that are important for this interaction. Furthermore, using surface plasmon resonance we measure the binding strength of PHYL1 Pn WB proteins to SEP3_K. Lastly, based on confocal images, we found that α-helix 2 of PHYL1 Pn WB plays an important role in PHYL1-mediated degradation of SEP3. Taken together, these results provide a structural understanding of the specific binding mechanism between PHYL1 Pn WB and SEP3_K.
Organizational Affiliation:
The PhD Program for Translational Medicine, College of Medical Science and Technology, Taipei Medical University and Academia Sinica, Taipei 11529, Taiwan.