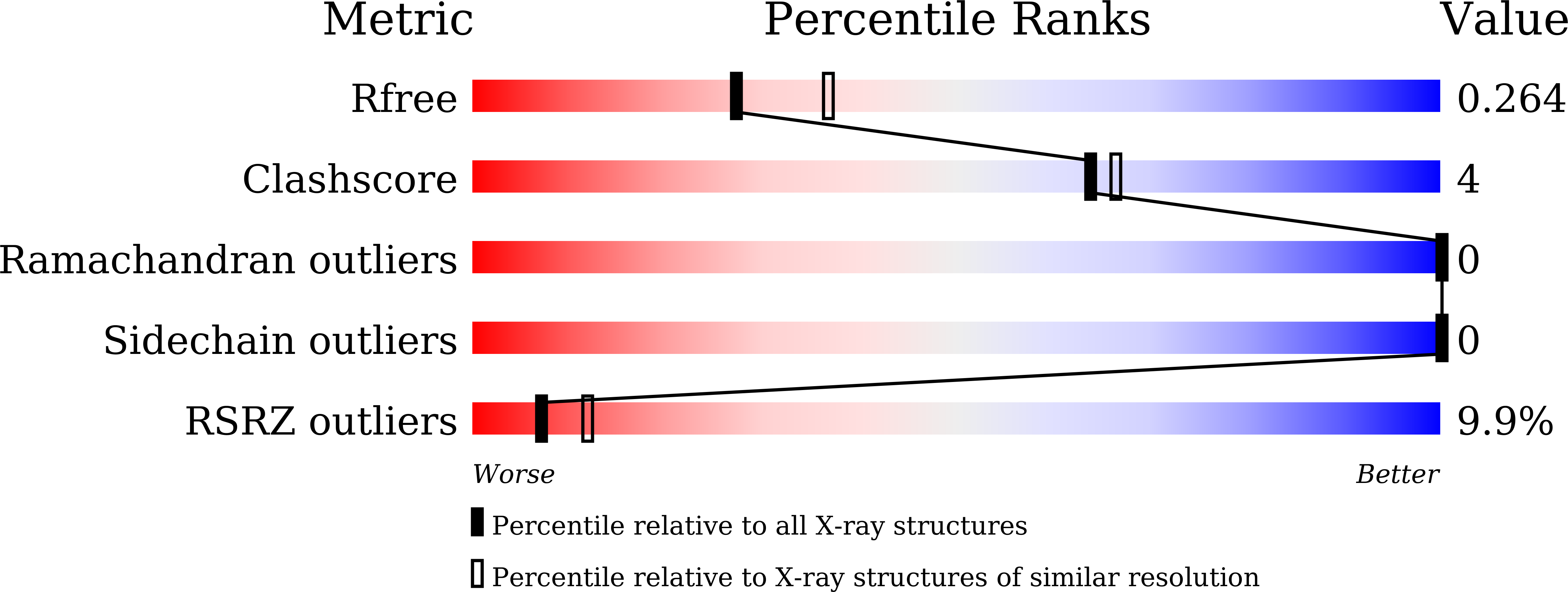
Synaptic Targeting and Function of SAPAPs Mediated by Phosphorylation-Dependent Binding to PSD-95 MAGUKs.
Zhu, J., Zhou, Q., Shang, Y., Li, H., Peng, M., Ke, X., Weng, Z., Zhang, R., Huang, X., Li, S.S.C., Feng, G., Lu, Y., Zhang, M.(2017) Cell Rep 21: 3781-3793
- PubMed: 29281827
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.107
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5YPO, 5YPR - PubMed Abstract:
The PSD-95/SAPAP/Shank complex functions as the major scaffold in orchestrating the formation and plasticity of the post-synaptic densities (PSDs). We previously demonstrated that the exquisitely specific SAPAP/Shank interaction is critical for Shank synaptic targeting and Shank-mediated synaptogenesis. Here, we show that the PSD-95/SAPAP interaction, SAPAP synaptic targeting, and SAPAP-mediated synaptogenesis require phosphorylation of the N-terminal repeat sequences of SAPAPs. The atomic structure of the PSD-95 guanylate kinase (GK) in complex with a phosphor-SAPAP repeat peptide, together with biochemical studies, reveals the molecular mechanism underlying the phosphorylation-dependent PSD-95/SAPAP interaction, and it also provides an explanation of a PSD-95 mutation found in patients with intellectual disabilities. Guided by the structural data, we developed potent non-phosphorylated GK inhibitory peptides capable of blocking the PSD-95/SAPAP interaction and interfering with PSD-95/SAPAP-mediated synaptic maturation and strength. These peptides are genetically encodable for investigating the functions of the PSD-95/SAPAP interaction in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Center for Protein Science Shanghai, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201203, China; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 333 Haike Road, Shanghai 201203, China; Division of Life Science, State Key Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Clear Water Bay, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China.