ACCORD: an assessment tool to determine the orientation of homodimeric coiled-coils.
Kim, B.W., Jung, Y.O., Kim, M.K., Kwon, D.H., Park, S.H., Kim, J.H., Kuk, Y.B., Oh, S.J., Kim, L., Kim, B.H., Yang, W.S., Song, H.K.(2017) Sci Rep 7: 43318-43318
- PubMed: 28266564
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43318
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
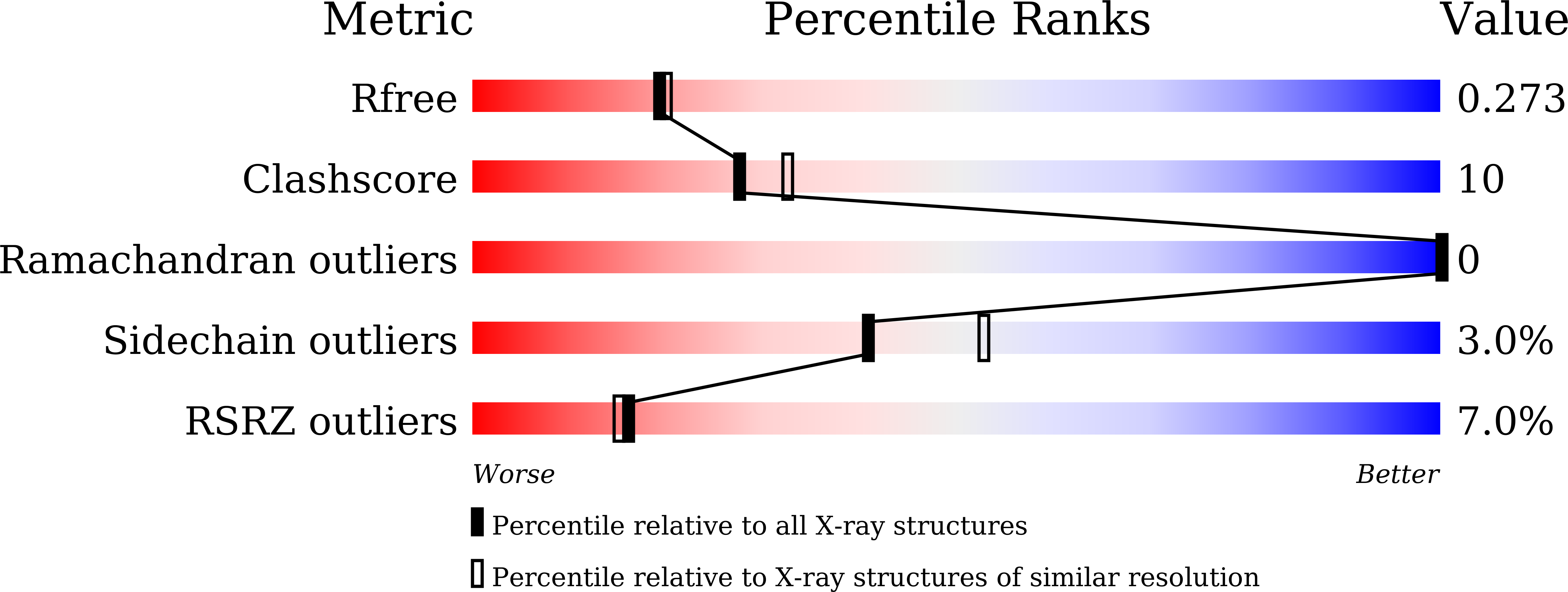
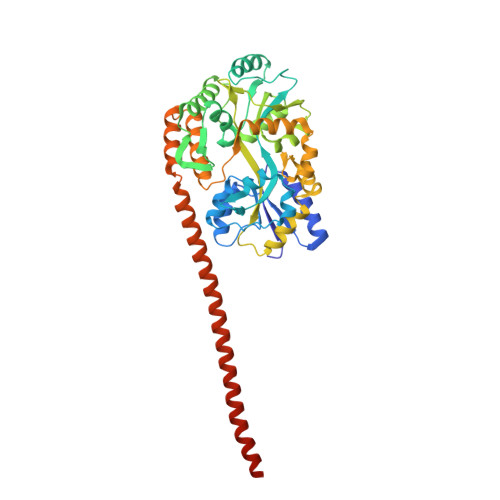
5JST - PubMed Abstract:
The coiled-coil (CC) domain is a very important structural unit of proteins that plays critical roles in various biological functions. The major oligomeric state of CCs is a dimer, which can be either parallel or antiparallel. The orientation of each α-helix in a CC domain is critical for the molecular function of CC-containing proteins, but cannot be determined easily by sequence-based prediction. We developed a biochemical method for assessing differences between parallel and antiparallel CC homodimers and named it ACCORD (Assessment tool for homodimeric Coiled-Coil ORientation Decision). To validate this technique, we applied it to 15 different CC proteins with known structures, and the ACCORD results identified these proteins well, especially with long CCs. Furthermore, ACCORD was able to accurately determine the orientation of a CC domain of unknown directionality that was subsequently confirmed by X-ray crystallography and small angle X-ray scattering. Thus, ACCORD can be used as a tool to determine CC directionality to supplement the results of in silico prediction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Life Sciences, Korea University, 145 Anam-ro, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 02841, Korea.