Structural basis of thiol-based regulation of formaldehyde detoxification in H. influenzae by a MerR regulator with no sensor region.
Counago, R.M., Chen, N.H., Chang, C.W., Djoko, K.Y., McEwan, A.G., Kobe, B.(2016) Nucleic Acids Res 44: 6981-6993
- PubMed: 27307602
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw543
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5D8C, 5D90, 5E01 - PubMed Abstract:
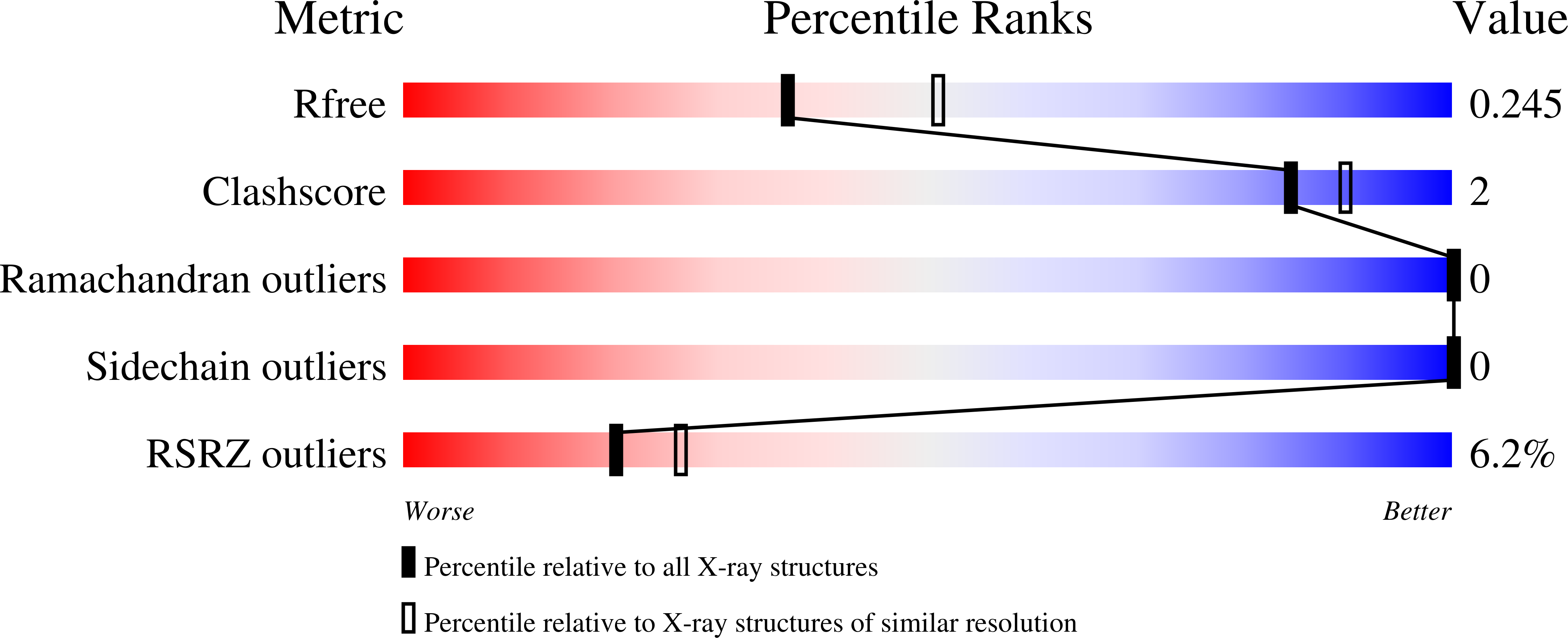
Pathogenic bacteria such as Haemophilus influenzae, a major cause of lower respiratory tract diseases, must cope with a range of electrophiles generated in the host or by endogenous metabolism. Formaldehyde is one such compound that can irreversibly damage proteins and DNA through alkylation and cross-linking and interfere with redox homeostasis. Its detoxification operates under the control of HiNmlR, a protein from the MerR family that lacks a specific sensor region and does not bind metal ions. We demonstrate that HiNmlR is a thiol-dependent transcription factor that modulates H. influenzae response to formaldehyde, with two cysteine residues (Cys54 and Cys71) identified to be important for its response against a formaldehyde challenge. We obtained crystal structures of HiNmlR in both the DNA-free and two DNA-bound forms, which suggest that HiNmlR enhances target gene transcription by twisting of operator DNA sequences in a two-gene operon containing overlapping promoters. Our work provides the first structural insights into the mechanism of action of MerR regulators that lack sensor regions.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Qld 4072, Australia Australian Infectious Diseases Research Centre, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Qld 4072, Australia Institute for Molecular Bioscience, University of Queensland, Brisbane, Qld 4072, Australia rafael.counago@sgc.ox.ac.uk.