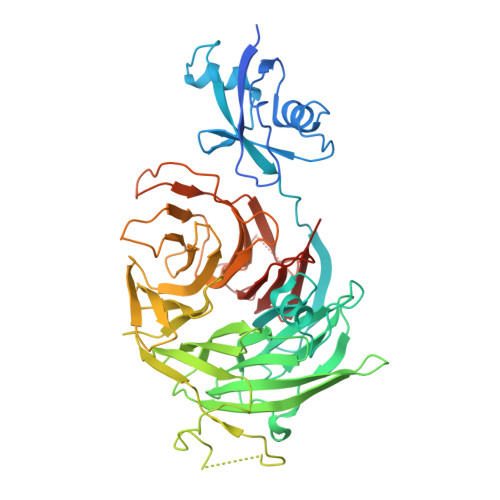
The structure of Erb1-Ytm1 complex reveals the functional importance of a high-affinity binding between two beta-propellers during the assembly of large ribosomal subunits in eukaryotes.
Wegrecki, M., Rodriguez-Galan, O., de la Cruz, J., Bravo, J.(2015) Nucleic Acids Res 43: 11017-11030
- PubMed: 26476442
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1043
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5CXB, 5CXC, 5CYK - PubMed Abstract:
Ribosome biogenesis is one of the most essential pathways in eukaryotes although it is still not fully characterized. Given the importance of this process in proliferating cells, it is obvious that understanding the macromolecular details of the interactions that take place between the assembly factors, ribosomal proteins and nascent pre-rRNAs is essentially required for the development of new non-genotoxic treatments for cancer. Herein, we have studied the association between the WD40-repeat domains of Erb1 and Ytm1 proteins. These are essential factors for the biogenesis of 60S ribosomal subunits in eukaryotes that form a heterotrimeric complex together with the also essential Nop7 protein. We provide the crystal structure of a dimer formed by the C-terminal part of Erb1 and Ytm1 from Chaetomium thermophilum at 2.1 Å resolution. Using a multidisciplinary approach we show that the β-propeller domains of these proteins interact in a novel manner that leads to a high-affinity binding. We prove that a point mutation within the interface of the complex impairs the interaction between the two proteins and negatively affects growth and ribosome production in yeast. Our study suggests insights into the association of the Erb1-Ytm1 dimer with pre-ribosomal particles.
Organizational Affiliation:
Instituto de Biomedicina de Valencia, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, c/ Jaime Roig 11, 46010 Valencia, Spain.