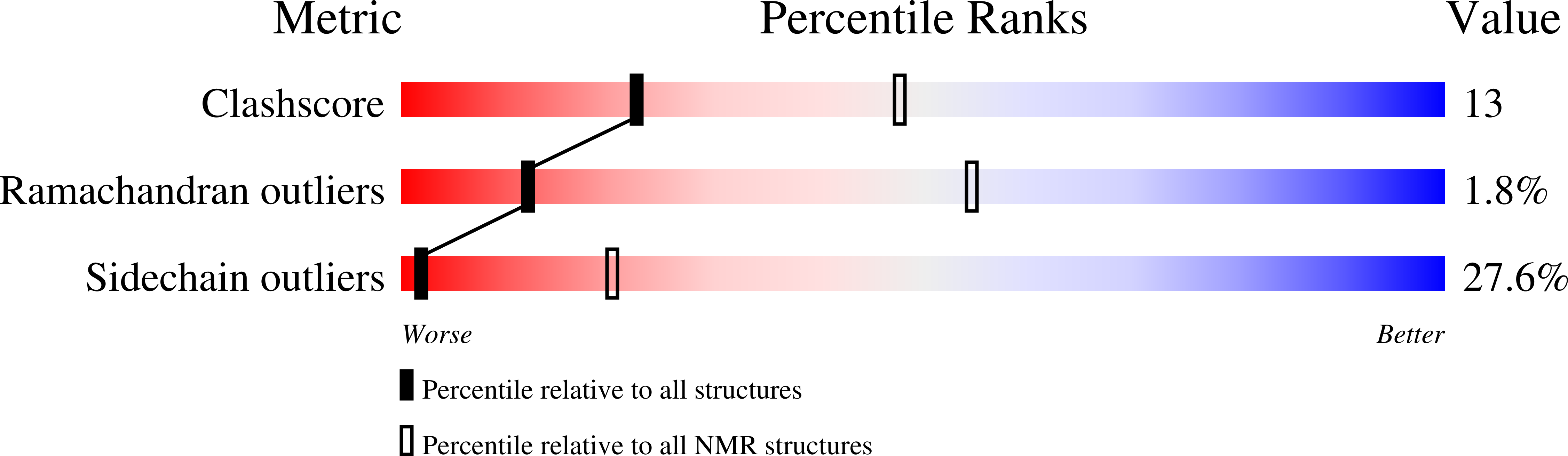Plant Villin Headpiece Domain Demonstrates a Novel Surface Charge Pattern and High Affinity for F-Actin.
Miears, H.L., Gruber, D.R., Horvath, N.M., Antos, J.M., Young, J., Sigurjonsson, J.P., Klem, M.L., Rosenkranz, E.A., Okon, M., McKnight, C.J., Vugmeyster, L., Smirnov, S.L.(2018) Biochemistry 57: 1690-1701
- PubMed: 29444403
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00856
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5VNT - PubMed Abstract:
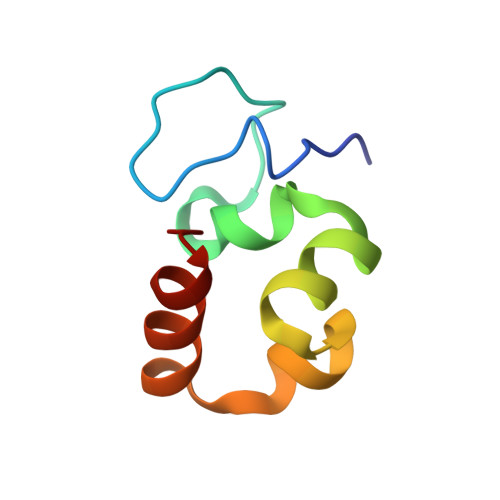
Plants utilize multiple isoforms of villin, an F-actin regulating protein with an N-terminal gelsolin-like core and a distinct C-terminal headpiece domain. Unlike their vertebrate homologues, plant villins have a much longer linker polypeptide connecting the core and headpiece. Moreover, the linker-headpiece connection region in plant villins lacks sequence homology to the vertebrate villin sequences. It is unknown to what extent the plant villin headpiece structure and function resemble those of the well-studied vertebrate counterparts. Here we present the first solution NMR structure and backbone dynamics characterization of a headpiece from plants, villin isoform 4 from Arabidopsis thaliana. The villin 4 headpiece is a 63-residue domain (V4HP63) that adopts a typical headpiece fold with an aromatics core and a tryptophan-centered hydrophobic cap within its C-terminal subdomain. However, V4HP63 has a distinct N-terminal subdomain fold as well as a novel, high mobility loop due to the insertion of serine residue in the canonical sequence that follows the variable length loop in headpiece sequences. The domain binds actin filaments with micromolar affinity, like the vertebrate analogues. However, the V4HP63 surface charge pattern is novel and lacks certain features previously thought necessary for high-affinity F-actin binding. Utilizing the updated criteria for strong F-actin binding, we predict that the headpiece domains of all other villin isoforms in A. thaliana have high affinity for F-actin.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry , Western Washington University , 516 High Street , Bellingham , Washington 98225-9150 , United States.