Structural Basis of Thermal Stability of the Tungsten Cofactor Synthesis Protein MoaB from Pyrococcus furiosus.
Havarushka, N., Fischer-Schrader, K., Lamkemeyer, T., Schwarz, G.(2014) PLoS One 9: e86030-e86030
- PubMed: 24465852
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086030
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
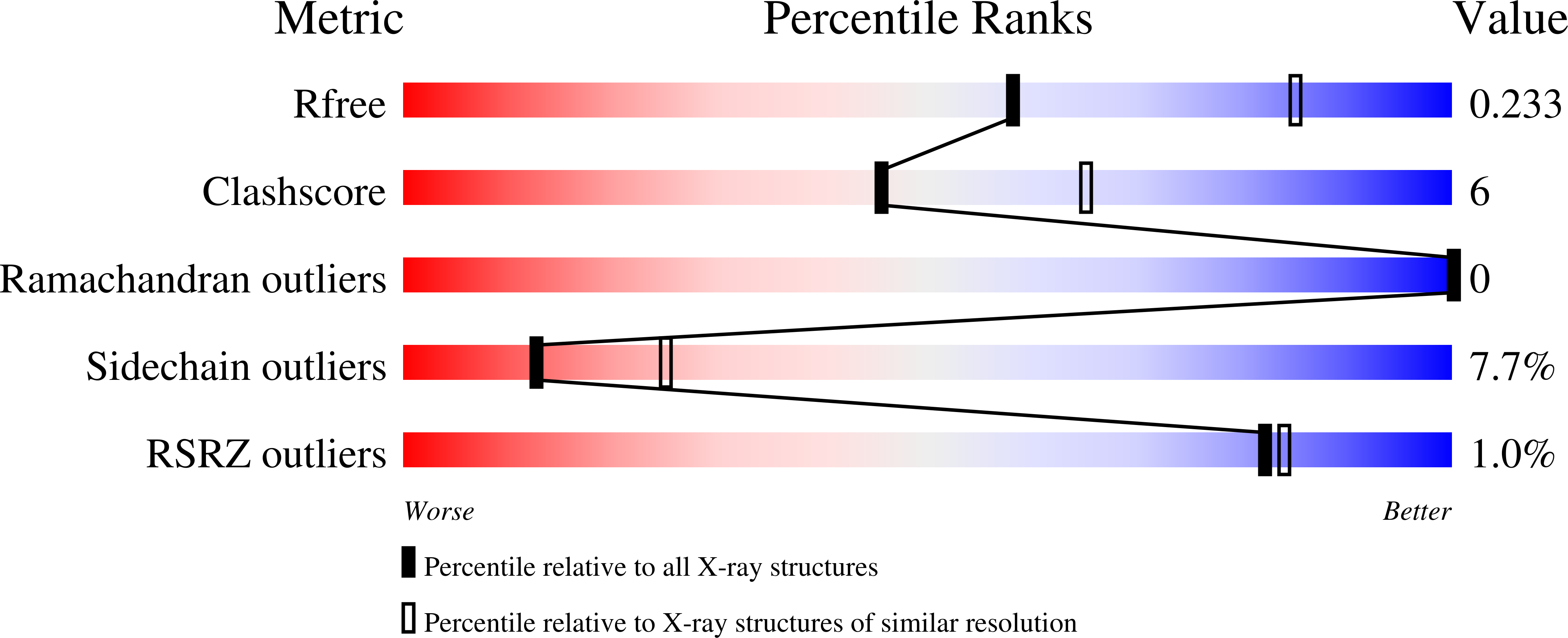
4LHB - PubMed Abstract:
Molybdenum and tungsten cofactors share a similar pterin-based scaffold, which hosts an ene-dithiolate function being essential for the coordination of either molybdenum or tungsten. The biosynthesis of both cofactors involves a multistep pathway, which ends with the activation of the metal binding pterin (MPT) by adenylylation before the respective metal is incorporated. In the hyperthermophilic organism Pyrococcus furiosus, the hexameric protein MoaB (PfuMoaB) has been shown to catalyse MPT-adenylylation. Here we determined the crystal structure of PfuMoaB at 2.5 Å resolution and identified key residues of α3-helix mediating hexamer formation. Given that PfuMoaB homologues from mesophilic organisms form trimers, we investigated the impact on PfuMoaB hexamerization on thermal stability and activity. Using structure-guided mutagenesis, we successfully disrupted the hexamer interface in PfuMoaB. The resulting PfuMoaB-H3 variant formed monomers, dimers and trimers as determined by size exclusion chromatography. Circular dichroism spectroscopy as well as chemical cross-linking coupled to mass spectrometry confirmed a wild-type-like fold of the protomers as well as inter-subunits contacts. The melting temperature of PfuMoaB-H3 was found to be reduced by more than 15 °C as determined by differential scanning calorimetry, thus demonstrating hexamerization as key determinant for PfuMoaB thermal stability. Remarkably, while a loss of activity at temperatures higher than 50 °C was observed in the PfuMoaB-H3 variant, at lower temperatures, we determined a significantly increased catalytic activity. The latter suggests a gain in conformational flexibility caused by the disruption of the hexamerization interface.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biochemistry, Department of Chemistry, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany.