Structure-function analysis of Staphylococcus aureus amidase reveals the determinants of peptidoglycan recognition and cleavage.
Buttner, F.M., Zoll, S., Nega, M., Gotz, F., Stehle, T.(2014) J Biol Chem 289: 11083-11094
- PubMed: 24599952
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.557306
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
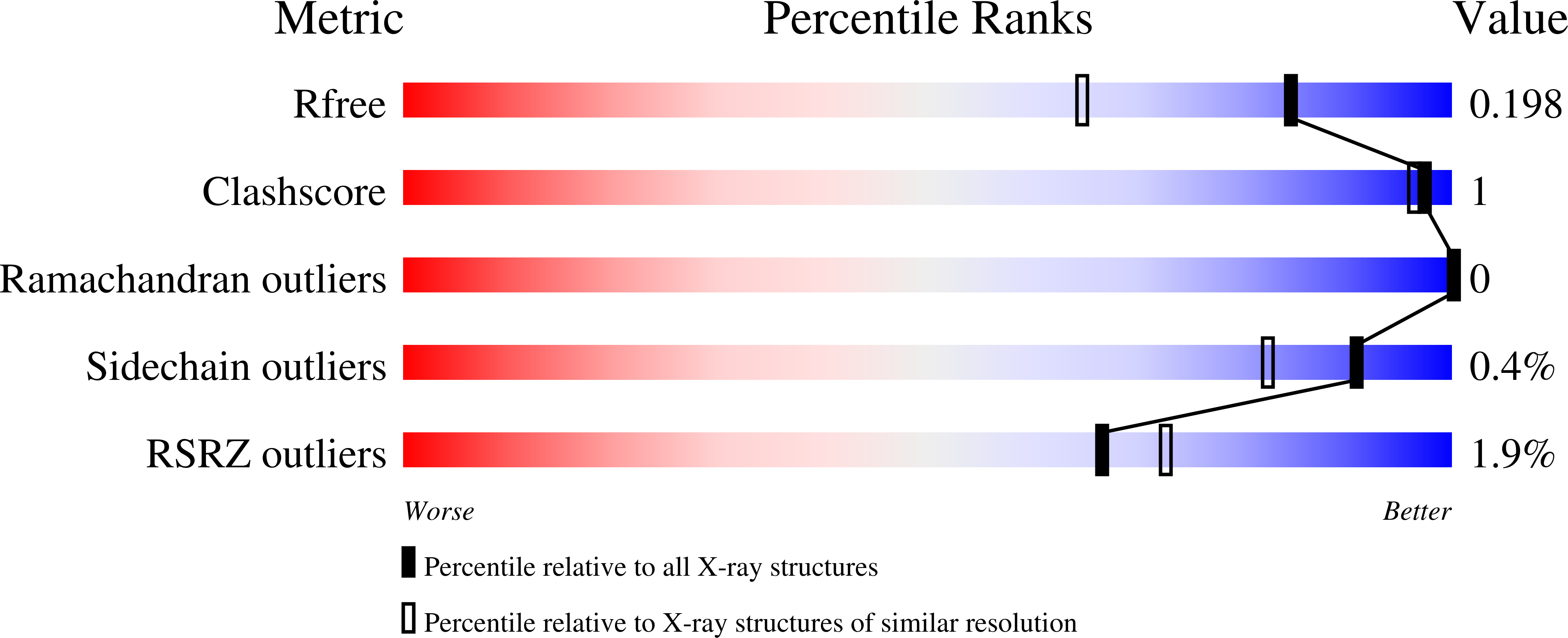
4KNK, 4KNL - PubMed Abstract:
The bifunctional major autolysin AtlA of Staphylococcus aureus cleaves the bacterium's peptidoglycan network (PGN) at two distinct sites during cell division. Deletion of the enzyme results in large cell clusters with disordered division patterns, indicating that AtlA could be a promising target for the development of new antibiotics. One of the two functions of AtlA is performed by the N-acetylmuramyl-l-alanine amidase AmiA, which cleaves the bond between the carbohydrate and the peptide moieties of PGN. To establish the structural requirements of PGN recognition and the enzymatic mechanism of cleavage, we solved the crystal structure of the catalytic domain of AmiA (AmiA-cat) in complex with a peptidoglycan-derived ligand at 1.55 Å resolution. The peptide stem is clearly visible in the structure, forming extensive contacts with protein residues by docking into an elongated groove. Less well defined electron density and the analysis of surface features indicate likely positions of the carbohydrate backbone and the pentaglycine bridge. Substrate specificity analysis supports the importance of the pentaglycine bridge for fitting into the binding cleft of AmiA-cat. PGN of S. aureus with l-lysine tethered with d-alanine via a pentaglycine bridge is completely hydrolyzed, whereas PGN of Bacillus subtilis with meso-diaminopimelic acid directly tethered with d-alanine is not hydrolyzed. An active site mutant, H370A, of AmiA-cat was completely inactive, providing further support for the proposed catalytic mechanism of AmiA. The structure reported here is not only the first of any bacterial amidase in which both the PGN component and the water molecule that carries out the nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the scissile bond are present; it is also the first peptidoglycan amidase complex structure of an important human pathogen.
Organizational Affiliation:
Interfaculty Institute of Biochemistry, University of Tübingen, Hoppe-Seyler-Strasse 4, 72076 Tübingen, Germany.