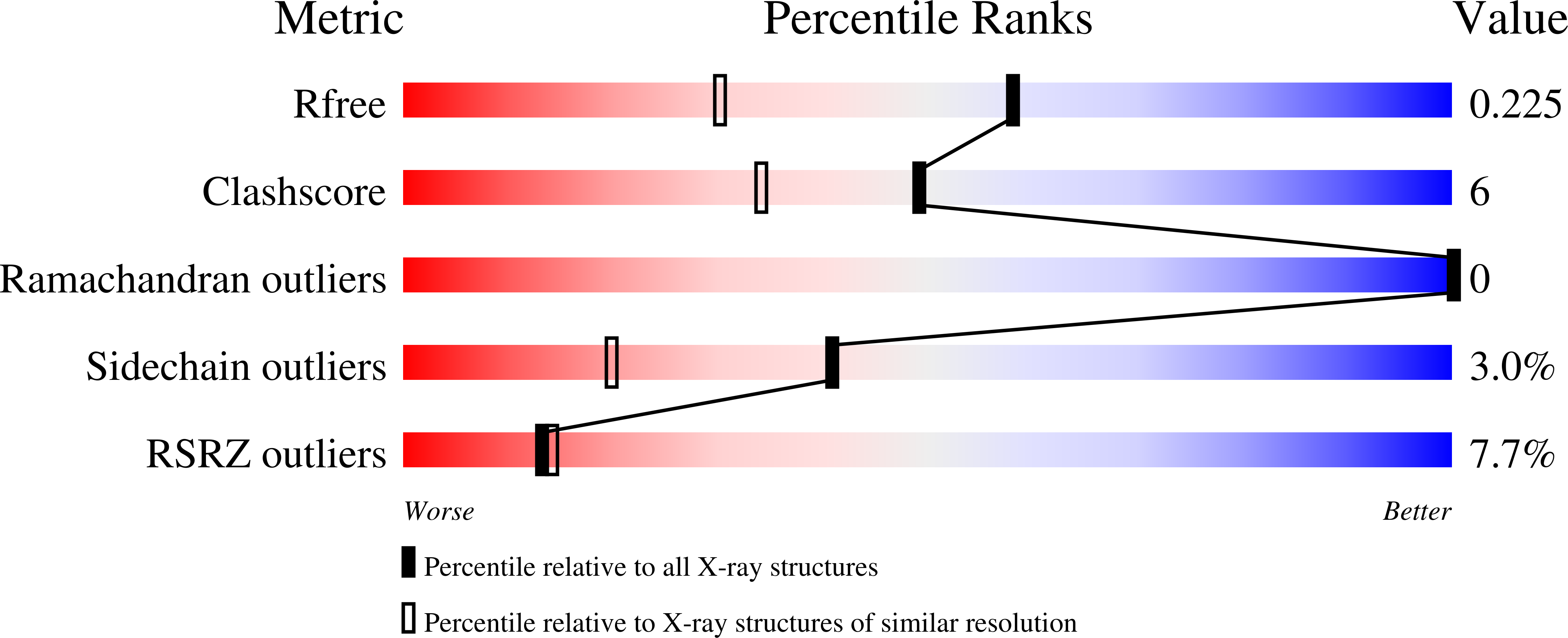
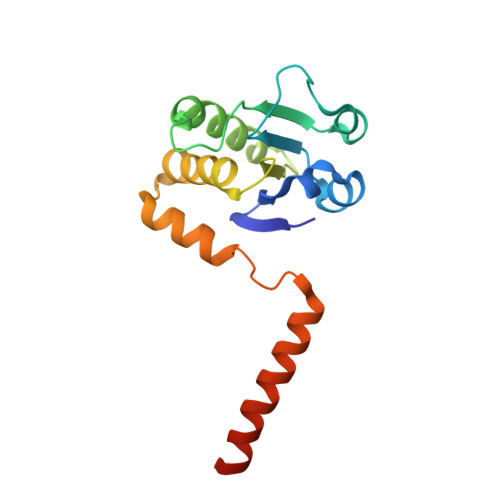
Atomic structure of dual-specificity phosphatase 26, a novel p53 phosphatase.
Lokareddy, R.K., Bhardwaj, A., Cingolani, G.(2013) Biochemistry 52: 938-948
- PubMed: 23298255
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi301476m
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4HRF - PubMed Abstract:
Regulation of p53 phosphorylation is critical to control its stability and biological activity. Dual-specificity phosphatase 26 (DUSP26) is a brain phosphatase highly overexpressed in neuroblastoma, which has been implicated in dephosphorylating phospho-Ser20 and phospho-Ser37 in the p53 transactivation domain. In this paper, we report the 1.68 Å crystal structure of a catalytically inactive mutant (Cys152Ser) of DUSP26 lacking the first 60 N-terminal residues (ΔN60-C/S-DUSP26). This structure reveals the architecture of a dual-specificity phosphatase domain related in structure to Vaccinia virus VH1. DUSP26 adopts a closed conformation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP)-binding loop, which results in an unusually shallow active site pocket and buried catalytic cysteine. A water molecule trapped inside the PTP-binding loop makes close contacts both with main chain and with side chain atoms. The hydrodynamic radius (R(H)) of ΔN60-C/S-DUSP26 measured from velocity sedimentation analysis (R(H) ∼ 22.7 Å) and gel filtration chromatography (R(H) ∼ 21.0 Å) is consistent with an ∼18 kDa globular monomeric protein. Instead in crystal, ΔN60-C/S-DUSP26 is more elongated (R(H) ∼ 37.9 Å), likely because of the extended conformation of C-terminal helix α9, which swings away from the phosphatase core to generate a highly basic surface. As in the case of phosphatase MKP-4, we propose that a substrate-induced conformational change, possibly involving rearrangement of helix α9 with respect to the phosphatase core, allows DUSP26 to adopt a catalytically active conformation. The structural characterization of DUSP26 presented in this paper provides the first atomic insight into this disease-associated phosphatase.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Thomas Jefferson University , 233 South 10th Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19107, United States.