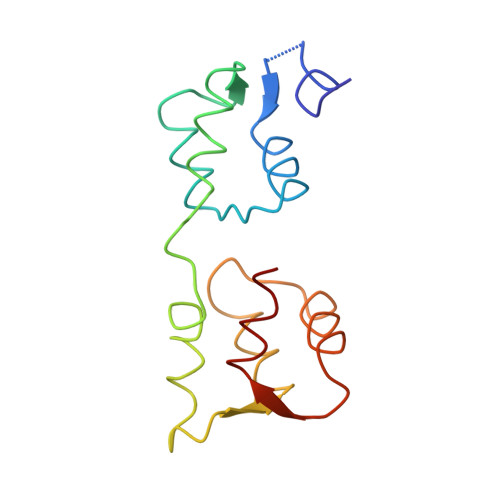
The structure of the D3 domain of Plasmodium falciparum myosin tail interacting protein MTIP in complex with a nanobody.
Khamrui, S., Turley, S., Pardon, E., Steyaert, J., Fan, E., Verlinde, C.L., Bergman, L.W., Hol, W.G.(2013) Mol Biochem Parasitol 190: 87-91
- PubMed: 23831371
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molbiopara.2013.06.003
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4GFT, 4GGN - PubMed Abstract:
Apicomplexan parasites enter host cells by many sophisticated steps including use of an ATP-powered invasion machinery. The machinery consists of multiple proteins, including a special myosin (MyoA) which moves along an actin fiber and which is connected to the myosin tail interaction protein (MTIP). Here we report a crystal structure of the major MyoA-binding domain (D3) of Plasmodium falciparum MTIP in complex with an anti-MTIP nanobody. In this complex, the MyoA-binding groove in MTIP-D3 is considerably less accessible than when occupied by the MyoA helix, due to a shift of two helices. The nanobody binds to an area slightly overlapping with the MyoA binding groove, covering a hydrophobic region next to the groove entrance. This provides a new avenue for arriving at compounds interfering with the invasion machinery since small molecules binding simultaneously to the nanobody binding site and the adjacent MyoA binding groove would prevent MyoA binding by MTIP.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Biomolecular Structure Center, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, United States.