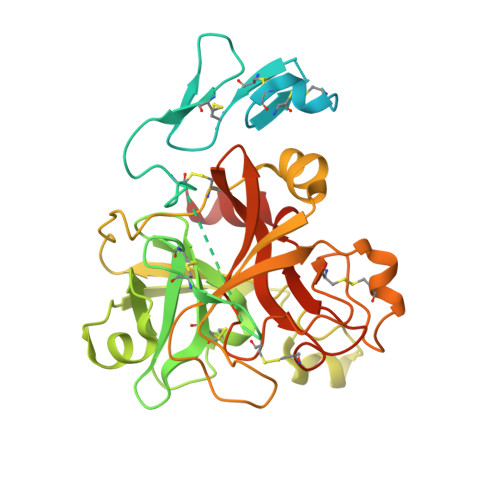
Crystal Structure of the Prothrombinase Complex from the Venom of Pseudonaja Textilis.
Lechtenberg, B.C., Murray-Rust, T.A., Johnson, D.J., Adams, T.E., Krishnaswamy, S., Camire, R.M., Huntington, J.A.(2013) Blood 122: 2777
- PubMed: 23869089
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-06-511733
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BXS, 4BXW - PubMed Abstract:
The prothrombinase complex, composed of the protease factor (f)Xa and cofactor fVa, efficiently converts prothrombin to thrombin by specific sequential cleavage at 2 sites. How the complex assembles and its mechanism of prothrombin processing are of central importance to human health and disease, because insufficient thrombin generation is the root cause of hemophilia, and excessive thrombin production results in thrombosis. Efforts to determine the crystal structure of the prothrombinase complex have been thwarted by the dependence of complex formation on phospholipid membrane association. Pseutarin C is an intrinsically stable prothrombinase complex preassembled in the venom gland of the Australian Eastern Brown Snake (Pseudonaja textilis). Here we report the crystal structures of the fX-fV complex and of activated fXa from P textilis venom and the derived model of active pseutarin C. Structural analysis supports a single substrate binding channel on fVa, to which prothrombin and the intermediate meizothrombin bind in 2 different orientations, providing insight into the architecture and mechanism of the prothrombinase complex-the molecular engine of blood coagulation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Haematology, Cambridge Institute for Medical Research, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom; and.