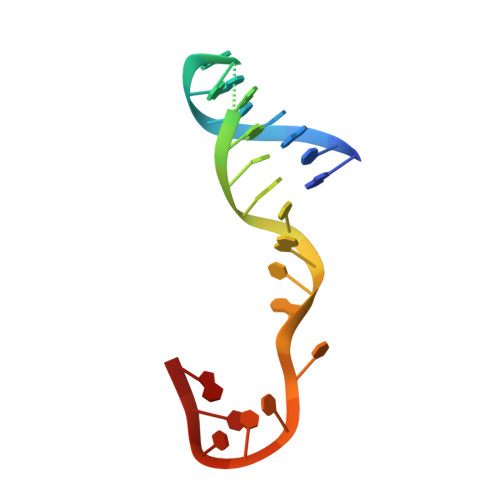
A high security double lock and key mechanism in HUH relaxases controls oriT-processing for plasmid conjugation.
Carballeira, J.D., Gonzalez-Perez, B., Moncalian, G., la Cruz, F.d.(2014) Nucleic Acids Res 42: 10632-10643
- PubMed: 25123661
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku741
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PCB - PubMed Abstract:
Relaxases act as DNA selection sieves in conjugative plasmid transfer. Most plasmid relaxases belong to the HUH endonuclease family. TrwC, the relaxase of plasmid R388, is the prototype of the HUH relaxase family, which also includes TraI of plasmid F. In this article we demonstrate that TrwC processes its target nic-site by means of a highly secure double lock and key mechanism. It is controlled both by TrwC-DNA intermolecular interactions and by intramolecular DNA interactions between several nic nucleotides. The sequence specificity map of the interaction between TrwC and DNA was determined by systematic mutagenesis using degenerate oligonucleotide libraries. The specificity map reveals the minimal nic sequence requirements for R388-based conjugation. Some nic-site sequence variants were still able to form the U-turn shape at the nic-site necessary for TrwC processing, as observed by X-ray crystallography. Moreover, purified TrwC relaxase effectively cleaved ssDNA as well as dsDNA substrates containing these mutant sequences. Since TrwC is able to catalyze DNA integration in a nic-site-containing DNA molecule, characterization of nic-site functionally active sequence variants should improve the search quality of potential target sequences for relaxase-mediated integration in any target genome.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departamento de Biología Molecular e Instituto de Biomedicina y Biotecnología de Cantabria, IBBTEC, Universidad de Cantabria-CSIC, C/Albert Einstein 22, 39011 Santander, Spain.