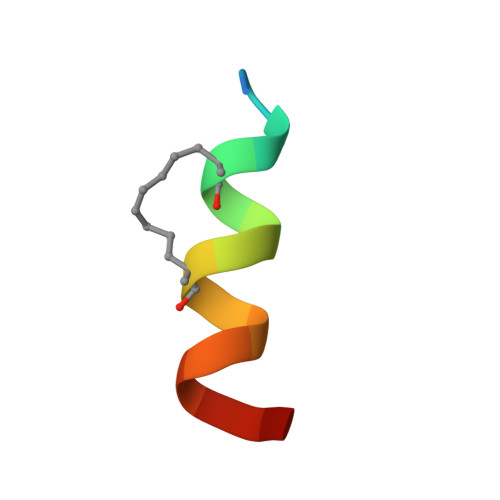
Inhibition of oncogenic Wnt signaling through direct targeting of beta-catenin.
Grossmann, T.N., Yeh, J.T., Bowman, B.R., Chu, Q., Moellering, R.E., Verdine, G.L.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 17942-17947
- PubMed: 23071338
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1208396109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DJS - PubMed Abstract:
Aberrant activation of signaling by the Wnt pathway is strongly implicated in the onset and progression of numerous types of cancer. Owing to the persistent dependence of these tumors on Wnt signaling for growth and survival, inhibition of this pathway is considered an attractive mechanism-based therapeutic approach. Oncogenic activation of Wnt signaling can ensue from a variety of distinct aberrations in the signaling pathway, but most share the common feature of causing increased cellular levels of β-catenin by interfering with its constitutive degradation. β-Catenin serves as a central hub in Wnt signaling by engaging in crucial protein-protein interactions with both negative and positive effectors of the pathway. Direct interference with these protein-protein interactions is a biologically compelling approach toward suppression of β-catenin hyperactivity, but such interactions have proven intransigent with respect to small-molecule targeting. Hence β-catenin remains an elusive target for translational cancer therapy. Here we report the discovery of a hydrocarbon-stapled peptide that directly targets β-catenin and interferes with its ability to serve as a transcriptional coactivator for T-cell factor (TCF) proteins, the downstream transcriptional regulators of the Wnt pathway.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Stem Cell and Regenerative Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA.