Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium Growth is Inhibited by the Concomitant Binding of Zn(II) and a Pyrrolyl-Hydroxamate to Znua, the Soluble Component of the Znuabc Transporter.
Ilari, A., Pescatori, L., Di Santo, R., Battistoni, A., Ammendola, S., Falconi, M., Berlutti, F., Valenti, P., Chiancone, E.(2016) Biochim Biophys Acta 1860: 534
- PubMed: 26691136
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.12.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
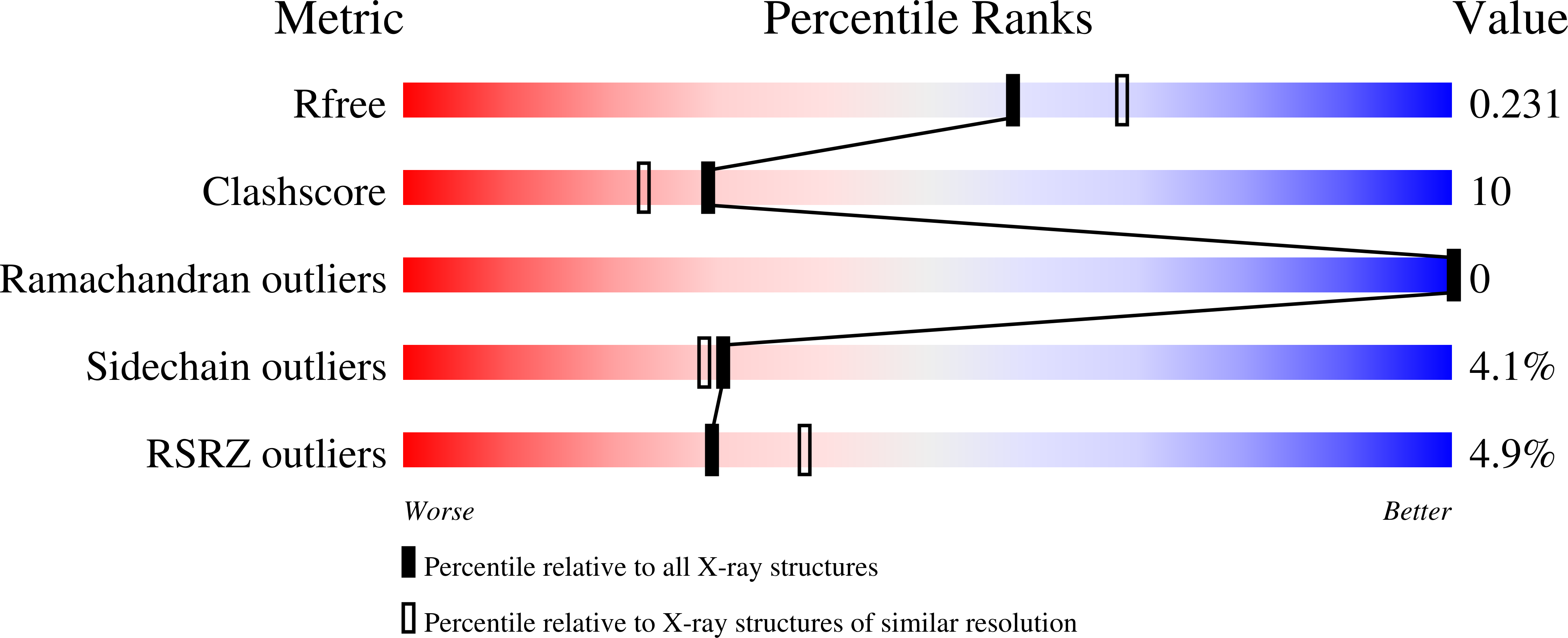
4BBP - PubMed Abstract:
Under conditions of Zn(II) deficiency, the most relevant high affinity Zn(II) transport system synthesized by many Gram-negative bacteria is the ZnuABC transporter. ZnuABC is absent in eukaryotes and plays an important role in bacterial virulence. Consequently, ZnuA, the periplasmic component of the transporter, appeared as a good target candidate to find new compounds able to contrast bacterial growth by interfering with Zn(II) uptake. Antibacterial activity assays on selected compounds from and in-house library against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC14028 were performed. The X-ray structure of the complex formed by SeZnuA with an active compound was solved at 2.15Å resolution. Two di-aryl pyrrole hydroxamic acids differing in the position of a chloride ion, RDS50 ([1-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-3-hydroxamic acid]) and RDS51 (1-[(2-chlorophenyl)methyl]-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-3-hydroxamic acid) were able to inhibit Salmonella growth and its invasion ability of Caco-2 cells. The X-ray structure of SeZnuA containing RDS51 revealed its presence at the metal binding site concomitantly with Zn(II) which is coordinated by protein residues and the hydroxamate moiety of the compound. Two molecules interfering with ZnuA-mediated Zn(II) transport in Salmonella have been identified for the first time. The resolution of the SeZnuA-RDS51 X-ray structure revealed that RDS51 is tightly bound both to the protein and to Zn(II) thereby inhibiting its release. These features pave the way to the rational design of new Zn(II)-binding drugs against Salmonella. The data reported show that targeting the bacterial ZnuABC transporter can represent a good strategy to find new antibiotics against Gram-negative bacteria.
Organizational Affiliation:
CNR-Institute of Molecular Biology and Pathology and Pasteur Institute Fondazione Cenci Bolognetti c/o Department of Biochemical Sciences, 'Sapienza' University of Rome, Piazzale A. Moro, 5, 00185 Rome, Italy. Electronic address: andrea.ilari@uniroma1.it.